CircRNA-vgll3 promotes osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via modulating miRNA-dependent integrin α5 expression
- PMID: 32814879
- PMCID: PMC7853044
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-020-0600-6
CircRNA-vgll3 promotes osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via modulating miRNA-dependent integrin α5 expression
Abstract
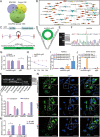
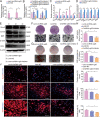
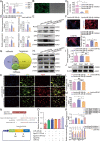
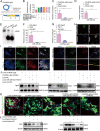
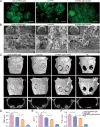
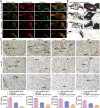
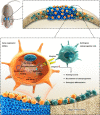
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) are promising candidate for regenerative medicine to repair non-healing bone defects due to their high and easy availability. However, the limited osteogenic differentiation potential greatly hinders the clinical application of ADSCs in bone repair. Accumulating evidences demonstrate that circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in stem/progenitor cell fate determination, but their specific role in stem/progenitor cell osteogenesis, remains mostly undescribed. Here, we show that circRNA-vgll3 originating from the vgll3 locus markedly enhances osteogenic differentiation of ADSCs; nevertheless, silencing of circRNA-vgll3 dramatically attenuates ADSC osteogenesis. Furthermore, we validate that circRNA-vgll3 functions in ADSC osteogenesis through a circRNA-vgll3/miR-326-5p/integrin α5 (Itga5) pathway. Itga5 promotes ADSC osteogenic differentiation and miR-326-5p suppresses Itga5 translation. CircRNA-vgll3 directly sequesters miR-326-5p in the cytoplasm and inhibits its activity to promote osteogenic differentiation. Moreover, the therapeutic potential of circRNA-vgll3-modified ADSCs with calcium phosphate cement (CPC) scaffolds was systematically evaluated in a critical-sized defect model in rats. Our results demonstrate that circRNA-vgll3 markedly enhances new bone formation with upregulated bone mineral density, bone volume/tissue volume, trabeculae number, and increased new bone generation. This study reveals the important role of circRNA-vgll3 during new bone biogenesis. Thus, circRNA-vgll3 engineered ADSCs may be effective potential therapeutic targets for bone regenerative medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

