White matter abnormalities across different epilepsy syndromes in adults: an ENIGMA-Epilepsy study
- PMID: 32814957
- PMCID: PMC7567169
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awaa200
White matter abnormalities across different epilepsy syndromes in adults: an ENIGMA-Epilepsy study
Abstract
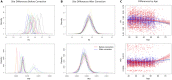
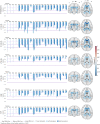
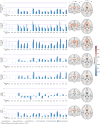
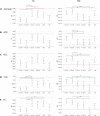
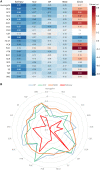
The epilepsies are commonly accompanied by widespread abnormalities in cerebral white matter. ENIGMA-Epilepsy is a large quantitative brain imaging consortium, aggregating data to investigate patterns of neuroimaging abnormalities in common epilepsy syndromes, including temporal lobe epilepsy, extratemporal epilepsy, and genetic generalized epilepsy. Our goal was to rank the most robust white matter microstructural differences across and within syndromes in a multicentre sample of adult epilepsy patients. Diffusion-weighted MRI data were analysed from 1069 healthy controls and 1249 patients: temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis (n = 599), temporal lobe epilepsy with normal MRI (n = 275), genetic generalized epilepsy (n = 182) and non-lesional extratemporal epilepsy (n = 193). A harmonized protocol using tract-based spatial statistics was used to derive skeletonized maps of fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity for each participant, and fibre tracts were segmented using a diffusion MRI atlas. Data were harmonized to correct for scanner-specific variations in diffusion measures using a batch-effect correction tool (ComBat). Analyses of covariance, adjusting for age and sex, examined differences between each epilepsy syndrome and controls for each white matter tract (Bonferroni corrected at P < 0.001). Across 'all epilepsies' lower fractional anisotropy was observed in most fibre tracts with small to medium effect sizes, especially in the corpus callosum, cingulum and external capsule. There were also less robust increases in mean diffusivity. Syndrome-specific fractional anisotropy and mean diffusivity differences were most pronounced in patients with hippocampal sclerosis in the ipsilateral parahippocampal cingulum and external capsule, with smaller effects across most other tracts. Individuals with temporal lobe epilepsy and normal MRI showed a similar pattern of greater ipsilateral than contralateral abnormalities, but less marked than those in patients with hippocampal sclerosis. Patients with generalized and extratemporal epilepsies had pronounced reductions in fractional anisotropy in the corpus callosum, corona radiata and external capsule, and increased mean diffusivity of the anterior corona radiata. Earlier age of seizure onset and longer disease duration were associated with a greater extent of diffusion abnormalities in patients with hippocampal sclerosis. We demonstrate microstructural abnormalities across major association, commissural, and projection fibres in a large multicentre study of epilepsy. Overall, patients with epilepsy showed white matter abnormalities in the corpus callosum, cingulum and external capsule, with differing severity across epilepsy syndromes. These data further define the spectrum of white matter abnormalities in common epilepsy syndromes, yielding more detailed insights into pathological substrates that may explain cognitive and psychiatric co-morbidities and be used to guide biomarker studies of treatment outcomes and/or genetic research.
Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging; epilepsy; multisite analysis; white matter.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Comment in
-
Epilepsy as a Disease of White Matter.Epilepsy Curr. 2020 Dec 3;21(1):27-29. doi: 10.1177/1535759720975744. eCollection 2021 Jan-Feb. Epilepsy Curr. 2020. PMID: 34025269 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abarrategui B, Parejo-Carbonell B, García García ME, Di Capua D, García-Morales I.. The cognitive phenotype of idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 2018; 89: 99–104. - PubMed
-
- Arfanakis K, Hermann BP, Rogers BP, Carew JD, Seidenberg M, Meyerand ME.. Diffusion tensor MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy. Magn Reson Imaging 2002; 20: 511–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS107739/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB015611/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M00841X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L016311/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K013998/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH121246/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD023696/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110347/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- FDN-154298/CIHR/Canada
- R01 AG059874/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH118514/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S00355X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 NS122827/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS065838/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH116147/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G0802012/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH117601/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/K023152/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R56 AG058854/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States

