Identification of novel therapeutic targets for blocking acantholysis in pemphigus
- PMID: 32815159
- PMCID: PMC7588822
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.15233
Identification of novel therapeutic targets for blocking acantholysis in pemphigus
Abstract
Background and purpose: Pemphigus is caused by autoantibodies against desmoglein (Dsg) 1, Dsg3, and/or non-Dsg antigens. Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is the most common manifestation of pemphigus, with painful erosions on mucous membranes. In most cases, blistering also occurs on the skin, leading to areas of extensive denudation. Despite improvements in pemphigus treatment, time to achieve remission is long, severe adverse events are frequent and 20% of patients do not respond adequately. Current clinical developments focus exclusively on modulating B cell function or autoantibody half-life. However, topical modulation of PV autoantibody-induced blistering is an attractive target because it could promptly relieve symptoms.
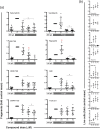
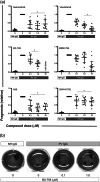
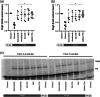
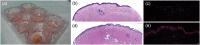
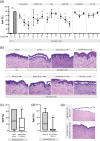
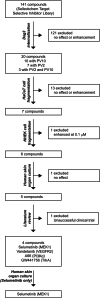
Experimental approach: To address this issue, we performed an unbiased screening in a complex biological system using 141 low MW inhibitors from a chemical library. Specifically, we evaluated PV IgG-induced Dsg3 internalization in HaCaT keratinocytes. Validation of the 20 identified compounds was performed using keratinocyte fragmentation assays, as well as a human skin organ culture (HSOC) model.
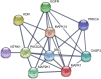
Key results: Overall, this approach led to the identification of four molecules involved in PV IgG-induced skin pathology: MEK1, TrkA, PI3Kα, and VEGFR2.
Conclusion and implications: This unbiased screening revealed novel mechanisms by which PV autoantibodies induce blistering in keratinocytes and identified new treatment targets for this severe and potentially life-threatening skin disease.
Keywords: autoimmunity; cell signaling; model system; pemphigus; skin.
© 2020 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
R.J.L. has received research funding from Miltenyi Biotec, Biogen, Biotest, Almirall, True North Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, ArgenX, TxCell, Topadur, Incyte, and Admirx and fees for consulting or speaking from ArgenX, Immunogenetics, Novartis, and Lilly. D.Z. has received support through research and development grants as well as for consulting or lecturing from Biotest, Fresenius, Miltenyi Biotec, Roche Pharma, Biogen, AbbVie, UCB, Janssen, Euroimmun, Dompe, Novartis, and ArgenX. C.M.H. is advisor to ArgenX and viDa Therapeutics. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander, S. P. H. , Roberts, R. E. , Broughton, B. R. S. , Sobey, C. G. , George, C. H. , Stanford, S. C. , … Ahluwalia, A. (2018). Goals and practicalities of immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry: A guide for submission to the British Journal of Pharmacology . British Journal of Pharmacology, 175(3), 407–411. 10.1111/bph.14112 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

