Physical and Chemical Factors Influencing the Printability of Hydrogel-based Extrusion Bioinks
- PMID: 32815369
- PMCID: PMC7673205
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00015
Physical and Chemical Factors Influencing the Printability of Hydrogel-based Extrusion Bioinks
Abstract
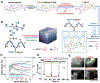
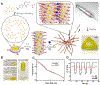
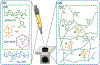
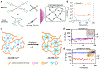
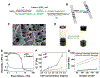
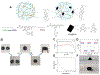
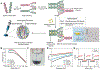
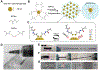
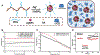
Bioprinting researchers agree that "printability" is a key characteristic for bioink development, but neither the meaning of the term nor the best way to experimentally measure it has been established. Furthermore, little is known with respect to the underlying mechanisms which determine a bioink's printability. A thorough understanding of these mechanisms is key to the intentional design of new bioinks. For the purposes of this review, the domain of printability is defined as the bioink requirements which are unique to bioprinting and occur during the printing process. Within this domain, the different aspects of printability and the factors which influence them are reviewed. The extrudability, filament classification, shape fidelity, and printing accuracy of bioinks are examined in detail with respect to their rheological properties, chemical structure, and printing parameters. These relationships are discussed and areas where further research is needed, are identified. This review serves to aid the bioink development process, which will continue to play a major role in the successes and failures of bioprinting, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine going forward.
Figures
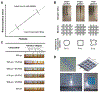

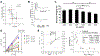
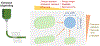
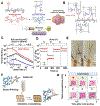





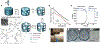
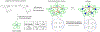





References
-
- Atala A; Kasper FK; Mikos AG Engineering Complex Tissues. Sci. Trans. Med. 2012, 4, 160rv112. - PubMed
-
- Arenas-Herrera JE; Ko IK; Atala A; Yoo JJ Decellularization for Whole Organ Bioengineering. Biomed. Mater 2013, 8, 014106. - PubMed
-
- Malda J; Visser J; Melchels FP; Jüngst T; Hennink WE; Dhert WJA; Groll J; Hutmacher DW Engineering Hydrogels for Biofabrication. Adv. Mater 2013, 25, 5011–5028. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

