Malaria Risk and Prevention in Asian Migrants to Angola
- PMID: 32815500
- PMCID: PMC7646810
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0706
Malaria Risk and Prevention in Asian Migrants to Angola
Abstract
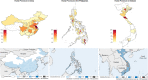
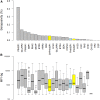
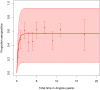
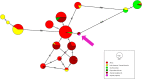
The number of Asian migrants working in sub-Saharan developing countries like Angola has been increasing. Their malaria risk, prevention, and care-seeking practices have not been characterized. A cross-sectional survey was conducted in 733 Chinese and Southeast Asian migrants in Angola. Respondents were interviewed and provided blood samples. Samples were analyzed to detect Plasmodium antigen and characterize host anti-Plasmodium response. Positive samples were genotyped using the pfs47 marker. Most respondents (72%; 95% CI: 68-75) reported using bed nets, but less than 1% reported using chemoprophylaxis. Depending on the assay, 1-4% of respondents had evidence of active malaria infection. By contrast, 55% (95% CI: 52-59) were seropositive for Plasmodium antibodies. Most infections were Plasmodium falciparum, but infection and/or exposure to Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium malariae was also detected. Seroprevalence by time in Angola showed most exposure occurred locally. One respondent had sufficiently high parasitemia for pfs47 genotyping, which showed that the infection was likely locally acquired despite recent travel to home country. Asian migrants to Angola are at substantial risk of malaria. Employers should consider enhanced malaria prevention programs, including chemoprophylaxis; embassies should encourage prevention practices. Angolan healthcare workers should be aware of high malaria exposure in Asian migrants.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclaimer: The findings and conclusion in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the CDC or the President’s Malaria Initiative. The authors declare they do not have any commercial or other associations that may pose a conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- African Development Bank , 2019. African Economic Outlook 2020: Developing Africa’s Workforce for the Future. Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire: African Development Bank–Building Today, A Better Africa Tomorrow; Available at: https://www.afdb.org/en/knowledge/publications/african-economic-outlook. Accessed March 20, 2020.
-
- International Labour Organization , 2019. Labour Migration in Africa. Geneva, Switzerland: International Labour Organization. Available at: http://www.ilo.org/africa/areas-of-work/labour-migration/WCMS_670561/lan.... Accessed March 20, 2020.
-
- International Organization for Migration , 2016. Glossary on Migration (2019). Grand-Saconnex, Switzerland: International Organization for Migration; Available at: https://www.iom.int/glossary-migration-2019. Accessed March 20, 2020.
-
- International Organization for Migration , 2020. World Migration Report 2020. Grand-Saconnex, Switzerland: IOM Online Bookstore; Available at: https://publications.iom.int/books/world-migration-report-2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

