3D virtual pathohistology of lung tissue from Covid-19 patients based on phase contrast X-ray tomography
- PMID: 32815517
- PMCID: PMC7473770
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60408
3D virtual pathohistology of lung tissue from Covid-19 patients based on phase contrast X-ray tomography
Abstract
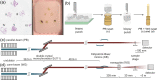
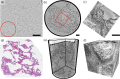
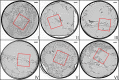
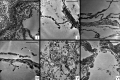
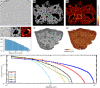
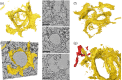
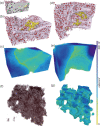
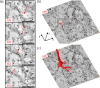
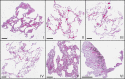
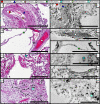
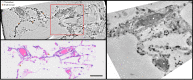
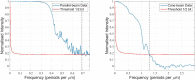
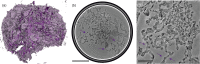
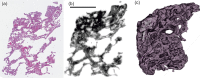
We present a three-dimensional (3D) approach for virtual histology and histopathology based on multi-scale phase contrast x-ray tomography, and use this to investigate the parenchymal architecture of unstained lung tissue from patients who succumbed to Covid-19. Based on this first proof-of-concept study, we propose multi-scale phase contrast x-ray tomography as a tool to unravel the pathophysiology of Covid-19, extending conventional histology by a third dimension and allowing for full quantification of tissue remodeling. By combining parallel and cone beam geometry, autopsy samples with a maximum cross section of 8 mm are scanned and reconstructed at a resolution and image quality, which allows for the segmentation of individual cells. Using the zoom capability of the cone beam geometry, regions-of-interest are reconstructed with a minimum voxel size of 167 nm. We exemplify the capability of this approach by 3D visualization of diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) with its prominent hyaline membrane formation, by mapping the 3D distribution and density of lymphocytes infiltrating the tissue, and by providing histograms of characteristic distances from tissue interior to the closest air compartment.
Keywords: 3d histology; Covid-19; human; immunology; inflammation; lung tissue; medicine; phase contrast; tomography; x-ray.
© 2020, Eckermann et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ME, JF, MR, MO, MS, FW, AT, MK, DJ, TS No competing interests declared
Figures

References
-
- Ackermann M, Verleden SE, Kuehnel M, Haverich A, Welte T, Laenger F, Vanstapel A, Werlein C, Stark H, Tzankov A, Li WW, Li VW, Mentzer SJ, Jonigk D. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19. New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;383:120–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bartels M, Hernandez VH, Krenkel M, Moser T, Salditt T. Phase contrast tomography of the mouse cochlea at Microfocus x-ray sources. Applied Physics Letters. 2013;103:083703. doi: 10.1063/1.4818737. - DOI
-
- Berg S, Kutra D, Kroeger T, Straehle CN, Kausler BX, Haubold C, Schiegg M, Ales J, Beier T, Rudy M, Eren K, Cervantes JI, Xu B, Beuttenmueller F, Wolny A, Zhang C, Koethe U, Hamprecht FA, Kreshuk A. Ilastik: interactive machine learning for (bio)image analysis. Nature Methods. 2019;16:1226–1232. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0582-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

