Characterization of Creatine Kinase Levels in Tofacitinib-Treated Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Results from Clinical Trials
- PMID: 32816215
- PMCID: PMC8298233
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-020-06560-4
Characterization of Creatine Kinase Levels in Tofacitinib-Treated Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Results from Clinical Trials
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Characterization of Creatine Kinase Levels in Tofacitinib‑Treated Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Results from Clinical Trials.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Sep;66(9):3214-3215. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06638-z. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33037970 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Tofacitinib is an oral, small-molecule JAK inhibitor for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC). Creatine kinase (CK) levels and CK-related adverse events (AEs) in tofacitinib-treated patients with UC were evaluated.
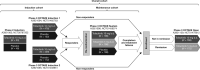
Methods: Data were analyzed for three UC cohorts: Induction (phase 2 and 3 induction studies); Maintenance (phase 3 maintenance study); Overall [patients who received tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (b.d.) in phase 2, phase 3, or open-label, long-term extension studies; data at November 2017]. Clinical trial data for tofacitinib-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis are presented for contextualization.
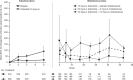
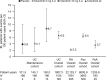
Results: Week 8 mean change from baseline CK with tofacitinib 10 mg b.d. induction therapy was 91.1 U/L (95% CI, 48.1-134.1) versus 19.2 U/L (8.5-29.9) with placebo. Among patients completing induction with 10 mg b.d. and re-randomized to 52 weeks of maintenance therapy, mean increases from induction baseline to the end of maintenance were 35.9 (8.1-63.7), 90.3 (51.9-128.7), and 115.6 U/L (91.6-139.7), with placebo, 5 and 10 mg b.d., respectively. The incidence rate (unique patients with events per 100 patient-years) for AEs of CK elevation in the tofacitinib-treated UC Overall cohort was 6.6 versus 2.2, 6.5, and 3.7 for tofacitinib-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and psoriatic arthritis, respectively. No serious AEs of CK elevation or AEs of myopathy occurred in UC studies.
Conclusions: In patients with UC, CK elevations with tofacitinib appeared reversible and not associated with clinically significant AEs. UC findings were consistent with tofacitinib use in other inflammatory diseases.
Trial registration: NCT00787202; NCT01465763; NCT01458951; NCT01458574; NCT01470612; NCT01262118; NCT01484561; NCT00147498; NCT00413660; NCT00550446; NCT00603512; NCT00687193; NCT01059864; NCT01164579; NCT00976599; NCT01359150; NCT02147587; NCT00960440; NCT00847613; NCT00814307; NCT00856544; NCT00853385; NCT01039688; NCT02187055; NCT00413699; NCT00661661; NCT01710046; NCT00678210; NCT01276639; NCT01309737; NCT01241591; NCT01186744; NCT01163253; NCT01877668; NCT01882439; NCT01976364.
Keywords: Creatine kinase; Inflammatory bowel disease; Safety; Tofacitinib; Ulcerative colitis.
© 2020. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
RP has received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Aptalis, AstraZeneca, Baxter, Biogen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Centocor, Cubist, Eisai, Elan, Ferring, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer Inc, Robarts Clinical Trials, Salix, Samsung Bioepis, Shire, Takeda, and UCB; has received research Grants from AbbVie, Ferring, Janssen, and Takeda; has received lectures and/or speaker bureau fees from AbbVie, Aptalis, AstraZeneca, Ferring, Janssen, Merck, Prometheus, Shire, and Takeda; and has received advisory board fees from Abbott, AbbVie, Amgen, Aptalis, AstraZeneca, Baxter, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Centocor, Cubist, Eisai, Elan, Ferring, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Merck, Pfizer Inc, Salix, Schering-Plough, Shire, Takeda, and UCB. JDI has been a consultant for, and/or has received research Grants or speaker fees from, AbbVie, Amgen, Eli Lilly, Gilead, Merck, Pfizer Inc, Roche, and UCB. LAC has served as a consultant for Pfizer Inc; has received research Grants from BioRad, Pfizer Inc, and PredictImmune; and has received advisory board fees from Gilead and Janssen. WW, AM, KK, LW, GC, and CS are employees and stockholders of Pfizer Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Kyriakides T, Angelini C, Schaefer J, et al. EFNS guidelines on the diagnostic approach to pauci- or asymptomatic hyperCKemia. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17:767–773. - PubMed
-
- Bagley WH, Yang H, Shah KH. Rhabdomyolysis. Intern Emerg Med. 2007;2:210–218. - PubMed
-
- Wong ET, Cobb C, Umehara MK, et al. Heterogeneity of serum creatine kinase activity among racial and gender groups of the population. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983;79:582–586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

