Inhibition of oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome by Saikosaponin-d alleviates acute liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in mice
- PMID: 32816567
- PMCID: PMC7444099
- DOI: 10.1177/2058738420950593
Inhibition of oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome by Saikosaponin-d alleviates acute liver injury in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatitis in mice
Abstract
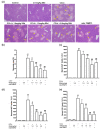
NLRP3 inflammasome activation results in severe liver inflammation and injury. Saikosaponin-d (SSd) possesses anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective effects. This study aimed to determine the protective effects of SSd on carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced acute liver injury in mice, and whether oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation participate in the process.The CCl4 mice model and controls were induced. The mice were treated with SSd at 1, 1.5, or 2.0 mg/kg in a total volume of 100 µl/25 g of body weight. Liver injury was assessed by histopathology. Oxidative stress was determined using mitochondrial superoxide production (MSP), malondialdehyde (MDA) content, and superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase (CAT) activities. NLRP3, ASC, and Caspase 1 were determined by real-time PCR and western blot. IL-1β and IL-18 levels were determined by ELISA.Significantly elevated oxidative stress was induced in the liver by CCl4, as demonstrated by histopathology and increases of MDA and MSP levels and decreases of SOD, GPx, and CAT activities (all P < 0.01). SSd significantly decreased the MDA and MSP levels and increased the activities of SOD, GPx, and CAT (all P < 0.05). The mRNA expression of NLRP3, ASC, and Caspase 1, and the protein expression of Caspase 1-p10, NLRP3, ASC, IL-1β, and IL-18 were significantly increased after CCl4 induction (all P < 0.01). These changes were reversed by SSd (all P < 0.05).Suppression of the oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation were involved in SSd-alleviated acute liver injury in CCl4-induced hepatitis.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; acute liver injury; carbon tetrachloride; mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; oxidative stress; saikosaponin-d.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Lee WM. (2012) Acute liver failure. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 33: 36–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

