Causal Inference Methods to Integrate Omics and Complex Traits
- PMID: 32816877
- PMCID: PMC8091955
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a040493
Causal Inference Methods to Integrate Omics and Complex Traits
Abstract
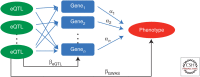
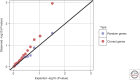
Major biotechnological advances have facilitated a tremendous boost to the collection of (gen-/transcript-/prote-/methyl-/metabol-)omics data in very large sample sizes worldwide. Coordinated efforts have yielded a deluge of studies associating diseases with genetic markers (genome-wide association studies) or with molecular phenotypes. Whereas omics-disease associations have led to biologically meaningful and coherent mechanisms, the identified (non-germline) disease biomarkers may simply be correlates or consequences of the explored diseases. To move beyond this realm, Mendelian randomization provides a principled framework to integrate information on omics- and disease-associated genetic variants to pinpoint molecular traits causally driving disease development. In this review, we show the latest advances in this field, flag up key challenges for the future, and propose potential solutions.
Copyright © 2021 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aguet F, Barbeira AN, Bonazzola R, Brown A, Castel SE, Jo B, Kasela S, Kim-Hellmuth S, Liang Y, Oliva M, et al. 2019. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. bioRxiv 787903. 10.1101/787903 - DOI
-
- Al Awam K, Haußleiter IS, Dudley E, Donev R, Brüne M, Juckel G, Thome J. 2015. Multiplatform metabolome and proteome profiling identifies serum metabolite and protein signatures as prospective biomarkers for schizophrenia. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 122: 111–122. 10.1007/s00702-014-1224-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allard C, Desgagné V, Patenaude J, Lacroix M, Guillemette L, Battista MC, Doyon M, Ménard J, Ardilouze JL, Perron P, et al. 2015. Mendelian randomization supports causality between maternal hyperglycemia and epigenetic regulation of leptin gene in newborns. Epigenetics 10: 342–351. 10.1080/15592294.2015.1029700 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barbeira AN, Dickinson SP, Bonazzola R, Zheng J, Wheeler HE, Torres JM, Torstenson ES, Shah KP, Garcia T, Edwards TL, et al. 2018. Exploring the phenotypic consequences of tissue specific gene expression variation inferred from GWAS summary statistics. Nat Commun 9: 1825. 10.1038/s41467-018-03621-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
