Elevated ACE-2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication
- PMID: 32817004
- PMCID: PMC7439429
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.01948-2020
Elevated ACE-2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication
Abstract
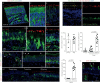
ACE2 protein is expressed at high levels in the human olfactory epithelium relative to upper airway epithelial cells. This may explain COVID-19-associated olfactory dysfunction, and suggests a SARS-CoV-2 reservoir site and potential intranasal therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Chen has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: W. Shen has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: N.R. Rowan has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: H. Kulaga has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A. Hillel has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: M. Ramanathan Jr has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: A.P. Lane has nothing to disclose.
Figures
Update of
-
Elevated ACE2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 9:2020.05.08.084996. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.08.084996. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Eur Respir J. 2020 Sep 24;56(3):2001948. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01948-2020. PMID: 32511390 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
