Vitamin K Supplementation to Improve Vascular Stiffness in CKD: The K4Kidneys Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32817311
- PMCID: PMC7609010
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020020225
Vitamin K Supplementation to Improve Vascular Stiffness in CKD: The K4Kidneys Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: Vascular calcification, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, is common among patients with CKD and is an independent contributor to increased vascular stiffness and vascular risk in this patient group. Vitamin K is a cofactor for proteins involved in prevention of vascular calcification. Whether or not vitamin K supplementation could improve arterial stiffness in patients with CKD is unknown.
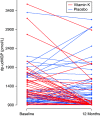
Methods: To determine if vitamin K supplementation might improve arterial stiffness in patients in CKD, we conducted a parallel-group, double-blind, randomized trial in participants aged 18 or older with CKD stage 3b or 4 (eGFR 15-45 ml/min per 1.73 m2). We randomly assigned participants to receive 400 μg oral vitamin K2 or matching placebo once daily for a year. The primary outcome was the adjusted between-group difference in carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity at 12 months. Secondary outcomes included augmentation index, abdominal aortic calcification, BP, physical function, and blood markers of mineral metabolism and vascular health. We also updated a recently published meta-analysis of trials to include the findings of this study.
Results: We included 159 randomized participants in the modified intention-to-treat analysis, with 80 allocated to receive vitamin K and 79 to receive placebo. Mean age was 66 years, 62 (39%) were female, and 87 (55%) had CKD stage 4. We found no differences in pulse wave velocity at 12 months, augmentation index at 12 months, BP, B-type natriuretic peptide, or physical function. The updated meta-analysis showed no effect of vitamin K supplementation on vascular stiffness or vascular calcification measures.
Conclusions: Vitamin K2 supplementation did not improve vascular stiffness or other measures of vascular health in this trial involving individuals with CKD.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: Vitamin K therapy to improve vascular health in patients with chronic kidney disease, ISRCTN21444964 (www.isrctn.com).
Keywords: arterial stiffness; chronic kidney disease; vascular calcification; vitamin K.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BR, Jafar TH, Heerspink HJ, Mann JF, et al. : Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 382: 339–352, 2013. - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K, van der Velde M, Astor BC, Woodward M, Levey AS, de Jong PE, et al. ; Chronic Kidney Disease Prognosis Consortium : Association of estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in general population cohorts: A collaborative meta-analysis. Lancet 375: 2073–2081, 2010. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Temmar M, Liabeuf S, Renard C, Czernichow S, Esper NE, Shahapuni I, et al. : Pulse wave velocity and vascular calcification at different stages of chronic kidney disease. J Hypertens 28: 163–169, 2010. - PubMed
-
- McEniery CM, McDonnell BJ, So A, Aitken S, Bolton CE, Munnery M, et al. ; Anglo-Cardiff Collaboration Trial Investigators : Aortic calcification is associated with aortic stiffness and isolated systolic hypertension in healthy individuals. Hypertension 53: 524–531, 2009. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

