Atypical TRAV1-2- T cell receptor recognition of the antigen-presenting molecule MR1
- PMID: 32817339
- PMCID: PMC7573270
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015292
Atypical TRAV1-2- T cell receptor recognition of the antigen-presenting molecule MR1
Abstract
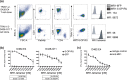
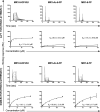
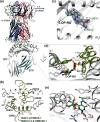
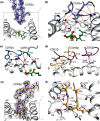
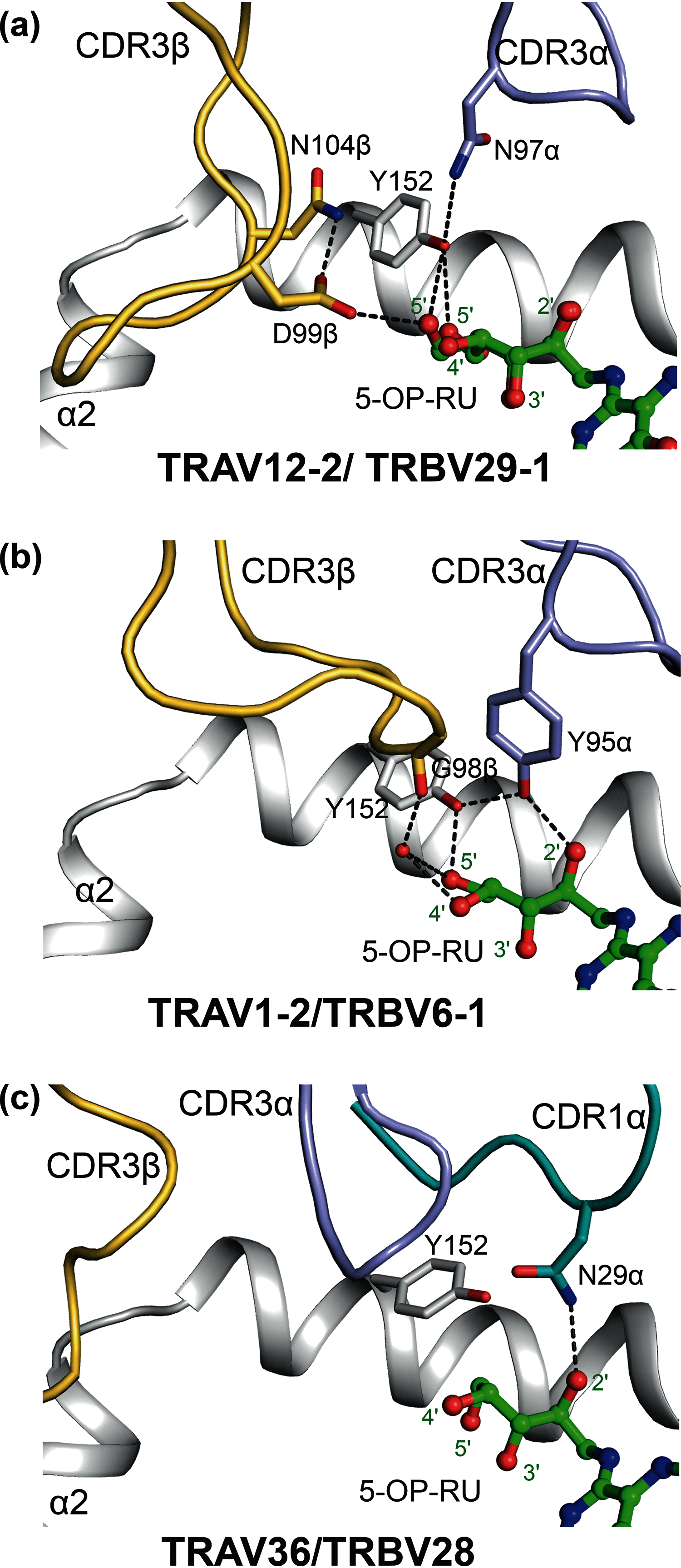
MR1 presents vitamin B-related metabolites to mucosal associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, which are characterized, in part, by the TRAV1-2+ αβ T cell receptor (TCR). In addition, a more diverse TRAV1-2- MR1-restricted T cell repertoire exists that can possess altered specificity for MR1 antigens. However, the molecular basis of how such TRAV1-2- TCRs interact with MR1-antigen complexes remains unclear. Here, we describe how a TRAV12-2+ TCR (termed D462-E4) recognizes an MR1-antigen complex. We report the crystal structures of the unliganded D462-E4 TCR and its complex with MR1 presenting the riboflavin-based antigen 5-OP-RU. Here, the TRBV29-1 β-chain of the D462-E4 TCR binds over the F'-pocket of MR1, whereby the complementarity-determining region (CDR) 3β loop surrounded and projected into the F'-pocket. Nevertheless, the CDR3β loop anchored proximal to the MR1 A'-pocket and mediated direct contact with the 5-OP-RU antigen. The D462-E4 TCR footprint on MR1 contrasted that of the TRAV1-2+ and TRAV36+ TCRs' docking topologies on MR1. Accordingly, diverse MR1-restricted T cell repertoire reveals differential docking modalities on MR1, thus providing greater scope for differing antigen specificities.
Keywords: : Antigen presentation; MAIT; MHC-related molecule (MR1); T-cell receptor (TCR); atypical MAIT TCR; crystal structure; immunology; major histocompatibility complex (MHC); protein structure; receptor structure-function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—J. R., J. M., L. L., and D. P. F. are named inventors on patent applications (PCT/AU2013/000742, WO2014005194) (PCT/AU2015/050148, WO2015149130) involving MR1 ligands for MR1-restricted MAIT cells owned by University of Queensland, Monash University, and University of Melbourne.
Figures

References
-
- Kjer-Nielsen L., Patel O., Corbett A. J., Le Nours J., Meehan B., Liu L., Bhati M., Chen Z., Kostenko L., Reantragoon R., Williamson N. A., Purcell A. W., Dudek N. L., McConville M. J., O'Hair R. A. J., et al. (2012) MR1 presents microbial vitamin B metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature 491, 717–723 10.1038/nature11605 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corbett A. J., Eckle S. B. G., Birkinshaw R. W., Liu L., Patel O., Mahony J., Chen Z., Reantragoon R., Meehan B., Cao H., Williamson N. A., Strugnell R. A., Van Sinderen D., Mak J. Y. W., Fairlie D. P., et al. (2014) T-cell activation by transitory neo-antigens derived from distinct microbial pathways. Nature 509, 361–365 10.1038/nature13160 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Eckle S. B. G., Birkinshaw R. W., Kostenko L., Corbett A. J., McWilliam H. E. G., Reantragoon R., Chen Z., Gherardin N. A., Beddoe T., Liu L., Patel O., Meehan B., Fairlie D. P., Villadangos J. A., Godfrey D. I., et al. (2014) A molecular basis underpinning the T cell receptor heterogeneity of mucosal-associated invariant T cells. J. Exp. Med. 211, 1585–1600 10.1084/jem.20140484 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harriff M. J., McMurtrey C., Froyd C. A., Jin H., Cansler M., Null M., Worley A., Meermeier E. W., Swarbrick G., Nilsen A., Lewinsohn D. A., Hildebrand W., Adams E. J., and Lewinsohn D. M. (2018) MR1 displays the microbial metabolome driving selective MR1-restricted T cell receptor usage. Sci. Immunol. 3, eaao2556 10.1126/sciimmunol.aao2556 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

