Quercetin negatively regulates IL-1β production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected human macrophages through the inhibition of MAPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways
- PMID: 32817626
- PMCID: PMC7446918
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237752
Quercetin negatively regulates IL-1β production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa-infected human macrophages through the inhibition of MAPK/NLRP3 inflammasome pathways
Abstract
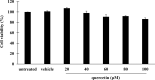
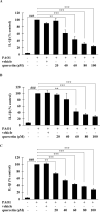
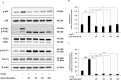
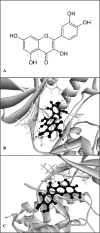
Pseudomonas aeruginosa remains a leading cause of nosocomial and serious life-threatening infections, and contributes to increased mortality in immunocompromised individuals. P. aeruginosa infection triggers host immune response and often provokes potent inflammatory mediators, which do not necessarily eradicate the causative pathogen. On the other hand, it causes severe airway damage and eventually decreased lung function. Such unfavorable outcomes of inflammatory injury have necessitated the development of novel effective agents that can combat with P. aeruginosa-mediated inflammation. Herein, we investigated the potential of quercetin in regulating P. aeruginosa-induced inflammation, with particular emphasized on the interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Our results showed that quercetin exerted the potent inhibitory activity against the production of IL-1β in macrophages infected by live P. aeruginosa PAO1, without exhibiting cytotoxicity. According to our settings, such the potent inhibitory activity of quercetin was clearly demonstrated through its ability to efficiently inhibit IL-1β during P. aeruginosa infection, pre- or even post-infection. In addition, quercetin strongly suppressed MAPK signaling pathway by inhibiting phosphorylation of the p38 MAPK and JNK2, and molecular docking study supported well with this observation. Moreover, quercetin reduced the NLRP3 expression and inhibited the P. aeruginosa-mediated cleavage of caspase-1 as well as mature IL-1β. These results thus indicated that quercetin inhibition of P. aeruginosa-induced IL-1β production is mediated by suppressing the initial priming step and by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Taken together, our findings demonstrated the promising regulatory activity of quercetin against IL-1β production in P. aeruginosa-infected macrophages, and indicated that quercetin has the potential to be effective as a novel therapeutic agent for treatment of P. aeruginosa-induced inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):471-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911403
-
Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome by lymphocytic microparticles via TLR4 pathway contributes to airway inflammation.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Jan 15;386(2):111737. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111737. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31759058
-
Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Nov;18(5):4399-4409. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9427. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30152849 Free PMC article.
-
Sendai Virus V Protein Inhibits the Secretion of Interleukin-1β by Preventing NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly.J Virol. 2018 Sep 12;92(19):e00842-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00842-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30021903 Free PMC article.
-
Immune escape strategies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to establish chronic infection.Cytokine. 2023 Mar;163:156135. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156135. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Cytokine. 2023. PMID: 36724716 Review.
Cited by
-
The relationship mammalian p38 with human health and its homolog Hog1 in response to environmental stresses in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Mar 10;13:1522294. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1522294. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40129568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids: Nutraceuticals for Rheumatic Diseases via Targeting of Inflammasome Activation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 6;22(2):488. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020488. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33418975 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential role of the antimicrobial peptide Tachyplesin III in regulating nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae-induced inflammation in airway epithelial cells.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Nov 19;206(12):471. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-04196-w. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39560721
-
Gallium-modified gelatin nanoparticles loaded with quercetin promote skin wound healing via the regulation of bacterial proliferation and macrophage polarization.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Jan 26;11:1124944. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1124944. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36777248 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Roles of Flavonoids in Caspase-11 Non-Canonical Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammatory Responses and Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 20;24(12):10402. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210402. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alhazmi A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa–Pathogenesis and pathogenic mechanisms. Int J Biol. 2015;7: 44–67.
-
- Eklöf J, Sørensen R, Ingebrigtsen TS, Sivapalan P, Achir I, Boel JB, et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and risk of death and exacerbations in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an observational cohort study of 22 053 patients. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26: 227–234. 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.06.011 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

