This is a preprint.
Vaccine optimization for COVID-19: who to vaccinate first?
- PMID: 32817963
- PMCID: PMC7430607
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.08.14.20175257
Vaccine optimization for COVID-19: who to vaccinate first?
Update in
-
Vaccine optimization for COVID-19: Who to vaccinate first?Sci Adv. 2021 Feb 3;7(6):eabf1374. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf1374. Print 2020 Feb. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 33536223 Free PMC article.
Abstract
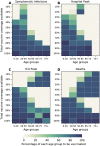
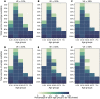
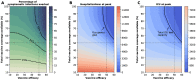
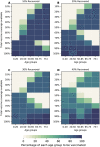
A vaccine, when available, will likely become our best tool to control the current COVID-19 pandemic. Even in the most optimistic scenarios, vaccine shortages will likely occur. Using an age-stratified mathematical model paired with optimization algorithms, we determined optimal vaccine allocation for four different metrics (deaths, symptomatic infections, and maximum non-ICU and ICU hospitalizations) under many scenarios. We find that a vaccine with effectiveness ≥50% would be enough to substantially mitigate the ongoing pandemic provided that a high percentage of the population is optimally vaccinated. When minimizing deaths, we find that for low vaccine effectiveness, irrespective of vaccination coverage, it is optimal to allocate vaccine to high-risk (older) age-groups first. In contrast, for higher vaccine effectiveness, there is a switch to allocate vaccine to high-transmission (younger) age-groups first for high vaccination coverage. While there are other societal and ethical considerations, this work can provide an evidence-based rationale for vaccine prioritization.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests We declare no competing interests.
Figures
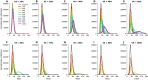
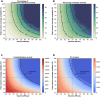
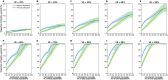
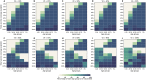
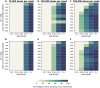
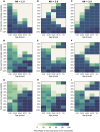
References
-
- Johns Hopkins University and Medicine. Coronavirus COVID-19 global cases by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU); 2020. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- Corum J, Grady D, Wee SL, Zimmer C. Coronavirus Vaccine Tracker; 2020. Available from: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/science/coronavirus-vaccine-tra....
-
- Cohen R, Jung C, Ouldali N, Sellam A, Corrard F, Aberrane S, et al. Assessment of spread of SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR and concomitant serology in children in a region heavily affected by COVID-19 pandemic. medRxiv. 2020;.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
