This is a preprint.
Detection, prevalence, and duration of humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 under conditions of limited population exposure
- PMID: 32817969
- PMCID: PMC7430613
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.08.14.20174490
Detection, prevalence, and duration of humoral responses to SARS-CoV-2 under conditions of limited population exposure
Update in
-
Orthogonal SARS-CoV-2 Serological Assays Enable Surveillance of Low-Prevalence Communities and Reveal Durable Humoral Immunity.Immunity. 2020 Nov 17;53(5):925-933.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.004. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 33129373 Free PMC article.
Abstract
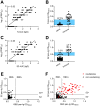
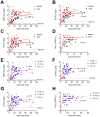
We conducted an extensive serological study to quantify population-level exposure and define correlates of immunity against SARS-CoV-2. We found that relative to mild COVID-19 cases, individuals with severe disease exhibited elevated authentic virus-neutralizing titers and antibody levels against nucleocapsid (N) and the receptor binding domain (RBD) and the S2 region of spike protein. Unlike disease severity, age and sex played lesser roles in serological responses. All cases, including asymptomatic individuals, seroconverted by 2 weeks post-PCR confirmation. RBD- and S2-specific and neutralizing antibody titers remained elevated and stable for at least 2-3 months post-onset, whereas those against N were more variable with rapid declines in many samples. Testing of 5882 self-recruited members of the local community demonstrated that 1.24% of individuals showed antibody reactivity to RBD. However, 18% (13/73) of these putative seropositive samples failed to neutralize authentic SARS-CoV-2 virus. Each of the neutralizing, but only 1 of the non-neutralizing samples, also displayed potent reactivity to S2. Thus, inclusion of multiple independent assays markedly improved the accuracy of antibody tests in low seroprevalence communities and revealed differences in antibody kinetics depending on the viral antigen. In contrast to other reports, we conclude that immunity is durable for at least several months after SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS:
Unrelated intellectual property of D.B. and Washington University has been licensed by Sana Biotechnology. J.N.Z. is on the scientific advisory board of and receives research funding from Young Blood Inc. R.S. is a founder and chief scientific officer of Geneticure. R.W. is currently an employee of Vir Biotechnology.
Figures


References
-
- Abbott R.K., Lee J.H., Menis S., Skog P., Rossi M., Ota T., Kulp D.W., Bhullar D., Kalyuzhniy O., Havenar-Daughton C., et al. (2018). Precursor Frequency and Affinity Determine B Cell Competitive Fitness in Germinal Centers, Tested with Germline-Targeting HIV Vaccine Immunogens. Immunity 48, 133–146.e6. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amanna I.J. (2007). Duration of Humoral Immunity to Common Viral and Vaccine Antigens. The New England Journal of Medicine 357, 1903–1915. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
