Instrument Gauge and Type in Uveal Melanoma Fine Needle Biopsy: Implications for Diagnostic Yield and Molecular Prognostication
- PMID: 32818452
- PMCID: PMC8117558
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajo.2020.08.014
Instrument Gauge and Type in Uveal Melanoma Fine Needle Biopsy: Implications for Diagnostic Yield and Molecular Prognostication
Abstract
Purpose: To systematically evaluate and compare the effects of using small-gauge needles and vitrectors on the ability to obtain adequate diagnostic and prognostic uveal melanoma biopsy specimens.
Design: Comparative evaluation of biopsy instruments.
Methods: Survival of uveal melanoma cells was evaluated in vitro following needle aspiration. Five therapeutically enucleated eyes were sampled in triplicate for ex vivo diagnostic biopsy experiments with 25 gauge (25 G) needle, 27 gauge (27 G) needle, and 27 G vitrector. During surgery in 8 patients, paired diagnostic transscleral fine needle aspiration biopsies were performed using both 25 G and 27 G needles. A review of cytologic specimens was performed by a panel of 3 expert cytopathologists. A retrospective chart review was performed to evaluate 100 consecutive tumors undergoing prognostic biopsy for gene expression profiling to assess the relationship between needle gauge and prognostic adequacy.
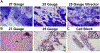
Results: No significant cell shearing of uveal melanoma cells occurred in vitro with 25 G, 27 G, or 30 G needles. For ex vivo biopsy samples, diagnostic yield was 100% using 25 G needle (5/5) or 27 G vitrector (5/5) but 60% using a 27 G needle (3/5). For in vivo samples, no difference in diagnostic yield was found between 25 G (75%, 6/8) or 27 G (75%, 6/8) needle sizes. Of 100 molecular prognostic biopsy samples evaluated, 65 were obtained using 27 G needles; for these biopsies, the prognostic yield was 65/65 (100%).
Conclusions: For diagnostic biopsy of uveal melanoma, a larger-gauge needle or a 27 G vitrector may have better overall cellularity and diagnostic yield when compared to a 27 G needle. However, for much more common molecular prognostic testing, a 27 G needle provided adequate sample in 100% (65/65) of cases, and a larger needle provided no additional benefit.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Yield, Techniques, and Complications of Transvitreal and Transscleral Biopsies in Small Uveal Melanoma.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018 May 1;136(5):482-488. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2018.0561. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29596552 Free PMC article.
-
The ocular consequences and applicability of minimally invasive 25-gauge transvitreal retinochoroidal biopsy.Ophthalmology. 2013 Dec;120(12):2565-2572. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.07.043. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Ophthalmology. 2013. PMID: 24053996
-
Fine-needle aspiration biopsy of uveal melanoma: outcomes and complications.Br J Ophthalmol. 2016 Apr;100(4):456-62. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306921. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016. PMID: 26231747
-
CHOROIDAL TUMOR BIOPSY: A Review of the Current State and a Glance Into Future Techniques.Retina. 2018 Sep;38 Suppl 1:S79-S87. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001997. Retina. 2018. PMID: 29280938 Review.
-
Uveal Melanoma Biopsy. A Review.Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2020 Winter;76(6):247-252. doi: 10.31348/2020/9. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2020. PMID: 33691424 Review. English.
Cited by
-
Integrative analysis identifies key genes related to metastasis and a robust gene-based prognostic signature in uveal melanoma.BMC Med Genomics. 2022 Mar 17;15(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12920-022-01211-1. BMC Med Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35300699 Free PMC article.
-
Uveal melanoma patient attitudes towards prognostic testing using gene expression profiling.Melanoma Manag. 2022 Sep 16;9(3):MMT62. doi: 10.2217/mmt-2022-0003. eCollection 2022 Sep. Melanoma Manag. 2022. PMID: 36147875 Free PMC article.
-
When less is more: the role of non-vitrectomized vitreous surgery in retinal diseases.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025 Aug 1;11(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40942-025-00686-1. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2025. PMID: 40751226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of Cytopathology Yield of Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy Using 25G Versus 27G Needles for Melanocytic Uveal Tumors.J Clin Med. 2025 May 23;14(11):3650. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113650. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507412 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights and Emerging Strategies for Treatment of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 25;12(10):2761. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102761. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32992823 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Accuracy of diagnosis of choroidal melanomas in the Collaborative Ocular Melanoma Study. COMS report no. 1. Arch Ophthalmol 1990;108(9):1268–1273. - PubMed
-
- Jensen OA, Prause JU, Scherfig E. Transvitreal retinochoroidal biopsy of suspected malignant lesions of the choroid. Follow-up of cases over 7 years. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 1997;75(4):409–411. - PubMed
-
- Cerbone L, Van Ginderdeuren R, Van den Oord J, et al. Clinical presentation, pathological features and natural course of metastatic uveal melanoma, an orphan and commonly fatal disease. Oncology 2014;86(3):185–189. - PubMed
-
- Kujala E, Makitie T, Kivela T. Very long-term prognosis of patients with malignant uveal melanoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003;44(11):4651–4659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

