Molecular origins of APOBEC-associated mutations in cancer
- PMID: 32818816
- PMCID: PMC7494591
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102905
Molecular origins of APOBEC-associated mutations in cancer
Abstract
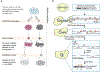
The APOBEC family of cytidine deaminases has been proposed to represent a major enzymatic source of mutations in cancer. Here, we summarize available evidence that links APOBEC deaminases to cancer mutagenesis. We also highlight newly identified human cell models of APOBEC mutagenesis, including cancer cell lines with suspected endogenous APOBEC activity and a cell system of telomere crisis-associated mutations. Finally, we draw on recent data to propose potential causes of APOBEC misregulation in cancer, including the instigating factors, the relevant mutator(s), and the mechanisms underlying generation of the genome-dispersed and clustered APOBEC-induced mutations.
Keywords: APOBEC mutations; Cancer cell lines; Cancer mutagenesis; Chromothripsis; Kataegis; Mutational signature.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Navaratnam N, Morrison JR, Bhattacharya S, Patel D, Funahashi T, Giannoni F, Teng BB, Davidson NO, Scott J, The p27 catalytic subunit of the apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme is a cytidine deaminase, J. Biol. Chem 268 (1993) 20709–20712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

