BuGZ facilitates loading of spindle assembly checkpoint proteins to kinetochores in early mitosis
- PMID: 32820050
- PMCID: PMC7586226
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013598
BuGZ facilitates loading of spindle assembly checkpoint proteins to kinetochores in early mitosis
Abstract
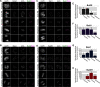
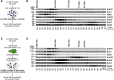
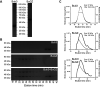
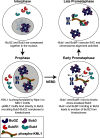
BuGZ is a kinetochore component that binds to and stabilizes Bub3, a key player in mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling. Bub3 is required for kinetochore recruitment of Bub1 and BubR1, two proteins that have essential and distinct roles in the checkpoint. Both Bub1 and BubR1 localize to kinetochores through interactions with Bub3, which are mediated through conserved GLEBS domains in both Bub1 and BubR1. BuGZ also has a GLEBS domain, which is required for its kinetochore localization as well, presumably mediated through Bub3 binding. Although much is understood about the requirements for Bub1 and BubR1 interaction with Bub3 and kinetochores, much less is known regarding BuGZ's requirements. Here, we used a series of mutants to demonstrate that BuGZ kinetochore localization requires only its core GLEBS domain, which is distinct from the requirements for both Bub1 and BubR1. Furthermore, we found that the kinetics of Bub1, BubR1, and BuGZ loading to kinetochores differ, with BuGZ localizing prior to BubR1 and Bub1. To better understand how complexes containing Bub3 and its binding partners are loaded to kinetochores, we carried out size-exclusion chromatography and analyzed Bub3-containing complexes from cells under different spindle assembly checkpoint signaling conditions. We found that prior to kinetochore formation, Bub3 is complexed with BuGZ but not Bub1 or BubR1. Our results point to a model in which BuGZ stabilizes Bub3 and promotes Bub3 loading onto kinetochores in early mitosis, which, in turn, facilitates Bub1 and BubR1 kinetochore recruitment and spindle assembly checkpoint signaling.
Keywords: BuGZ; Bub1; Bub3; BubR1; cell biology; cell division; checkpoint control; kinetochore mitosis; spindle assembly checkpoint.
© 2020 Shirnekhi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest—The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A microtubule-associated zinc finger protein, BuGZ, regulates mitotic chromosome alignment by ensuring Bub3 stability and kinetochore targeting.Dev Cell. 2014 Feb 10;28(3):268-81. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.12.013. Epub 2014 Jan 23. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24462186 Free PMC article.
-
Two functionally distinct kinetochore pools of BubR1 ensure accurate chromosome segregation.Nat Commun. 2016 Jul 26;7:12256. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12256. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27457023 Free PMC article.
-
The human spindle assembly checkpoint protein Bub3 is required for the establishment of efficient kinetochore-microtubule attachments.Mol Biol Cell. 2008 Apr;19(4):1798-813. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e07-07-0633. Epub 2008 Jan 16. Mol Biol Cell. 2008. PMID: 18199686 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetochore-microtubule interactions "in check" by Bub1, Bub3 and BubR1: The dual task of attaching and signalling.Cell Cycle. 2008 Jun 15;7(12):1763-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.7.12.6180. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Cell Cycle. 2008. PMID: 18594200 Review.
-
The spindle checkpoint proteins BUB1 and BUBR1: (SLiM)ming down to the basics.Trends Biochem Sci. 2022 Apr;47(4):352-366. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2022.01.004. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Trends Biochem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35184951 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ubiquitin-protein ligase UBR5 in the disassembly of mitotic checkpoint complexes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022 Mar 1;119(9):e2121478119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2121478119. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022. PMID: 35217622 Free PMC article.
-
A bifunctional kinase-phosphatase module balances mitotic checkpoint strength and kinetochore-microtubule attachment stability.EMBO J. 2023 Oct 16;42(20):e112630. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112630. Epub 2023 Sep 15. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37712330 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of Bub3 gene in malignant tumors.Cell Biol Int. 2022 May;46(5):673-682. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11740. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Cell Biol Int. 2022. PMID: 34882895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aurora-A condensation mediated by BuGZ aids its mitotic centrosome functions.iScience. 2024 Apr 18;27(5):109785. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109785. eCollection 2024 May 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38746663 Free PMC article.
-
Parthenolide disrupts mitosis by inhibiting ZNF207/BUGZ-promoted kinetochore-microtubule attachment.EMBO J. 2025 Jul;44(13):3764-3793. doi: 10.1038/s44318-025-00469-2. Epub 2025 May 27. EMBO J. 2025. PMID: 40425854 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

