Designed protein logic to target cells with precise combinations of surface antigens
- PMID: 32820060
- PMCID: PMC8085813
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aba6527
Designed protein logic to target cells with precise combinations of surface antigens
Abstract
Precise cell targeting is challenging because most mammalian cell types lack a single surface marker that distinguishes them from other cells. A solution would be to target cells using specific combinations of proteins present on their surfaces. In this study, we design colocalization-dependent protein switches (Co-LOCKR) that perform AND, OR, and NOT Boolean logic operations. These switches activate through a conformational change only when all conditions are met, generating rapid, transcription-independent responses at single-cell resolution within complex cell populations. We implement AND gates to redirect T cell specificity against tumor cells expressing two surface antigens while avoiding off-target recognition of single-antigen cells, and three-input switches that add NOT or OR logic to avoid or include cells expressing a third antigen. Thus, de novo designed proteins can perform computations on the surface of cells, integrating multiple distinct binding interactions into a single output.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
M.J.L., S.E.B., A.I.S., J.B., R.A.L., M.G., C.E.C., S.R.R., and D.B. are inventors on patents related to this work. M.J.L., S.E.B., A.I.S., R.A.L., M.J.B., S.R.R., and D.B. hold equity in Lyell Immunopharma. D.B. holds equity in Sana Biotechnology. M.J.L., S.E.B., R.A.L., M.J.B., and S.R.R. are employees of Lyell Immunopharma. A.I.S. is a consultant of Lyell Immunopharma.
Figures
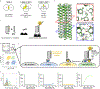
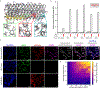


Comment in
-
When de novo-designed protein logics meet CAR-T therapies.Cell Res. 2020 Nov;30(11):946-947. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-00419-z. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32978606 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

