Structural basis of transcription-translation coupling
- PMID: 32820061
- PMCID: PMC7566311
- DOI: 10.1126/science.abb5317
Structural basis of transcription-translation coupling
Abstract
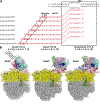
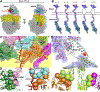
In bacteria, transcription and translation are coupled processes in which the movement of RNA polymerase (RNAP)-synthesizing messenger RNA (mRNA) is coordinated with the movement of the first ribosome-translating mRNA. Coupling is modulated by the transcription factors NusG (which is thought to bridge RNAP and the ribosome) and NusA. Here, we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of Escherichia coli transcription-translation complexes (TTCs) containing different-length mRNA spacers between RNAP and the ribosome active-center P site. Structures of TTCs containing short spacers show a state incompatible with NusG bridging and NusA binding (TTC-A, previously termed "expressome"). Structures of TTCs containing longer spacers reveal a new state compatible with NusG bridging and NusA binding (TTC-B) and reveal how NusG bridges and NusA binds. We propose that TTC-B mediates NusG- and NusA-dependent transcription-translation coupling.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures


Comment in
-
A short and long distance relationship.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020 Nov;18(11):603. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00445-z. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32887947 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

