4-Phenylbutyrate ameliorates apoptotic neural cell death in Down syndrome by reducing protein aggregates
- PMID: 32820178
- PMCID: PMC7441064
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-70362-x
4-Phenylbutyrate ameliorates apoptotic neural cell death in Down syndrome by reducing protein aggregates
Abstract
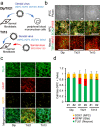
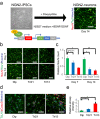
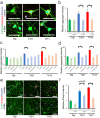
Individuals with Down syndrome (DS) commonly show unique pathological phenotypes throughout their life span. Besides the specific effects of dosage-sensitive genes on chromosome 21, recent studies have demonstrated that the gain of a chromosome exerts an adverse impact on cell physiology, regardless of the karyotype. Although dysregulated transcription and perturbed protein homeostasis are observed in common in human fibroblasts with trisomy 21, 18, and 13, whether and how this aneuploidy-associated stress acts on other cell lineages and affects the pathophysiology are unknown. Here, we investigated cellular stress responses in human trisomy 21 and 13 neurons differentiated from patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cells. Neurons of both trisomies showed increased vulnerability to apoptotic cell death, accompanied by dysregulated protein homeostasis and upregulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. In addition, misfolded protein aggregates, comprising various types of neurodegenerative disease-related proteins, were abnormally accumulated in trisomic neurons. Intriguingly, treatment with sodium 4-phenylbutyrate, a chemical chaperone, successfully decreased the formation of protein aggregates and prevented the progression of cell apoptosis in trisomic neurons. These results suggest that aneuploidy-associated stress might be a therapeutic target for the neurodegenerative phenotypes in DS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal’s policy and have the following competing interests. Dr. Mahito Nakanishi is the founder and chief technology officer of Tokiwa-Bio, Inc. Ms. Manami Ohtaka is an employee of Tokiwa-Bio, Inc. The method to generate iPS cells with the SeVdp vector installing reprogramming genes is protected by the following patents: JP 4936482, JP 5633075, JP 5963309, US 9145564, US 8496941 B2, US 9365866 B2, EP 2434012, and EP 2639297. This does not alter our adherence to all the
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

