Prognostic value of depression and anxiety on breast cancer recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 282,203 patients
- PMID: 32820237
- PMCID: PMC7714689
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-020-00865-6
Prognostic value of depression and anxiety on breast cancer recurrence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 282,203 patients
Abstract
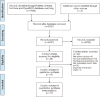
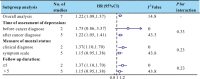
Depression and anxiety are common comorbidities in breast cancer patients. Whether depression and anxiety are associated with breast cancer progression or mortality is unclear. Herein, based on a systematic literature search, 17 eligible studies involving 282,203 breast cancer patients were included. The results showed that depression was associated with cancer recurrence [1.24 (1.07, 1.43)], all-cause mortality [1.30 (1.23, 1.36)], and cancer-specific mortality [1.29 (1.11, 1.49)]. However, anxiety was associated with recurrence [1.17 (1.02, 1.34)] and all-cause mortality [1.13 (1.07, 1.19)] but not with cancer-specific mortality [1.05 (0.82, 1.35)]. Comorbidity of depression and anxiety is associated with all-cause mortality [1.34 (1.24, 1.45)] and cancer-specific mortality [1.45 (1.11, 1.90)]. Subgroup analyses demonstrated that clinically diagnosed depression and anxiety, being female and of younger age (<60 years), and shorter follow-up duration (≤5 years) were related to a poorer prognosis. Our study highlights the critical role of depression/anxiety as an independent factor in predicting breast cancer recurrence and survival. Further research should focus on a favorable strategy that works best to improve outcomes among breast cancer patients with mental disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- DeSantis CE, Bray F, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Anderson BO, Jemal A. International variation in female breast cancer incidence and mortality rates. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2015;24:1495–506. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Qadir H, Austin PC, Lee DS, Amir E, Tu JV, Thavendiranathan P, et al. A population-based study of cardiovascular mortality following early-stage breast cancer. JAMA Cardiol. 2017;2:88–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

