Thallium-201 Imaging in Intact Olfactory Sensory Neurons with Reduced Pre-Synaptic Inhibition In Vivo
- PMID: 32820461
- PMCID: PMC7541386
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-020-02078-y
Thallium-201 Imaging in Intact Olfactory Sensory Neurons with Reduced Pre-Synaptic Inhibition In Vivo
Abstract
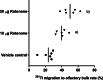
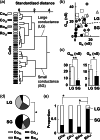
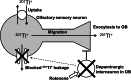
In this study, we determined whether the 201Tl (thallium-201)-based olfactory imaging is affected if olfactory sensory neurons received reduced pre-synaptic inhibition signals from dopaminergic interneurons in the olfactory bulb in vivo. The thallium-201 migration rate to the olfactory bulb and the number of action potentials of olfactory sensory neurons were assessed 3 h following left side nasal administration of rotenone, a mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I inhibitor that decreases the number of dopaminergic interneurons without damaging the olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory bulb, in mice (6-7 animals per group). The migration rate of thallium-201 to the olfactory bulb was significantly increased following intranasal administration of thallium-201 and rotenone (10 μg rotenone, p = 0.0012; 20 μg rotenone, p = 0.0012), compared with that in control mice. The number of action potentials was significantly reduced in the olfactory sensory neurons in the rotenone treated side of 20 μg rotenone-treated mice, compared with that in control mice (p = 0.0029). The migration rate of thallium-201 to the olfactory bulb assessed with SPECT-CT was significantly increased in rats 24 h after the left intranasal administration of thallium-201 and 100 μg rotenone, compared with that in control rats (p = 0.008, 5 rats per group). Our results suggest that thallium-201 migration to the olfactory bulb is increased in intact olfactory sensory neurons with reduced pre-synaptic inhibition from dopaminergic interneurons in olfactory bulb glomeruli.
Keywords: Action potential; Dopaminergic interneuron; Olfactory dysfunction; Olfactory transport; Rotenone; Tyrosine hydroxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Intranasal administration of rotenone in mice attenuated olfactory functions through the lesion of dopaminergic neurons in the olfactory bulb.Neurotoxicology. 2015 Dec;51:106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.10.006. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 26493152
-
Intranasal Administration of Rotenone to Mice Induces Dopaminergic Neurite Degeneration of Dopaminergic Neurons in the Substantia Nigra.Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(1):108-112. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00654. Biol Pharm Bull. 2017. PMID: 28049942
-
Assessment of olfactory nerve by SPECT-MRI image with nasal thallium-201 administration in patients with olfactory impairments in comparison to healthy volunteers.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057671. Epub 2013 Feb 28. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23469046 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Presynaptic inhibition of olfactory sensory neurons: new mechanisms and potential functions.Chem Senses. 2013 Jul;38(6):459-74. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt018. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Chem Senses. 2013. PMID: 23761680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic inhibition of olfactory receptor neurons in crustaceans.Microsc Res Tech. 2002 Aug 15;58(4):365-75. doi: 10.1002/jemt.10144. Microsc Res Tech. 2002. PMID: 12214303 Review.
Cited by
-
Intranasal delivery of imaging agents to the brain.Theranostics. 2024 Aug 19;14(13):5022-5101. doi: 10.7150/thno.98473. eCollection 2024. Theranostics. 2024. PMID: 39267777 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shiga H, Taki J, Washiyama K, Yamamoto J, Kinase S, Okuda K, Kinuya S, Watanabe N, et al. Assessment of olfactory nerve by SPECT-MRI image with nasal thallium-201 administration in patients with olfactory impairments in comparison to healthy volunteers. PLoS One. 2013;8:e57671. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057671. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

