A Deep-Learning Approach for Automated OCT En-Face Retinal Vessel Segmentation in Cases of Optic Disc Swelling Using Multiple En-Face Images as Input
- PMID: 32821471
- PMCID: PMC7401896
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.2.17
A Deep-Learning Approach for Automated OCT En-Face Retinal Vessel Segmentation in Cases of Optic Disc Swelling Using Multiple En-Face Images as Input
Abstract
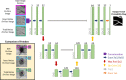
Purpose: In cases of optic disc swelling, segmentation of projected retinal blood vessels from optical coherence tomography (OCT) volumes is challenging due to swelling-based shadowing artifacts. Based on our hypothesis that simultaneously considering vessel information from multiple projected retinal layers can substantially increase vessel visibility, in this work, we propose a deep-learning-based approach to segment vessels involving the simultaneous use of three OCT en-face images as input.
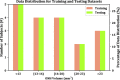
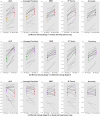
Methods: A human expert vessel tracing combining information from OCT en-face images of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), inner retina, and total retina as well as a registered fundus image served as the reference standard. The deep neural network was trained from the imaging data from 18 patients with optic disc swelling to output a vessel probability map from three OCT en-face input images. The vessels from the OCT en-face images were also manually traced in three separate stages to compare with the performance of the proposed approach.
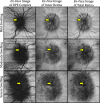
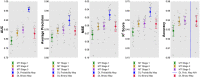
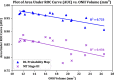
Results: On an independent volume-matched test set of 18 patients, the proposed deep-learning-based approach outperformed the three OCT-based manual tracing stages. The manual tracing based on three OCT en-face images also outperformed the manual tracing using only the traditional RPE en-face image.
Conclusions: In cases of optic disc swelling, use of multiple en-face images enables better vessel segmentation when compared with the traditional use of a single en-face image.
Translational relevance: Improved vessel segmentation approaches in cases of optic disc swelling can be used as features for an improved assessment of the severity and cause of the swelling.
Keywords: U-Net; deep learning; multiple en-face images; optic disc swelling; optical coherence tomography; papilledema; retinal blood vessels; vessel segmentation.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: M.S. Islam, None; J.-K. Wang, None; S.S. Johnson, None; M.J. Thurtell, None; R.H. Kardon, Fight for Sight, Inc. (S), Department of Veterans Affairs Research Foundation, Iowa City, IA (S); M.K. Garvin, University of Iowa (P)
Figures

References
-
- Van Stavern GP. Optic disc edema. Semin Neurol. 2007; 27: 233–243. - PubMed
-
- Hayreh SS. Optic disc edema in raised intracranial pressure, V: pathogenesis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977; 95: 1553–1565. - PubMed
-
- Trobe JD. Papilledema: the vexing issues. J Neuroophthalmol. 2011; 31: 175–186. - PubMed
-
- Scott CJ, Kardon RH, Lee AG, et al. .. Diagnosis and grading of papilledema in patients with raised intracranial pressure using optical coherence tomography vs clinical expert assessment using a clinical staging scale. Arch Ophthalmol. 2010; 128: 705–711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

