2018 Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Korea
- PMID: 32821702
- PMCID: PMC7379116
- DOI: 10.12997/jla.2019.8.2.78
2018 Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Korea
Abstract
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
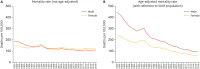
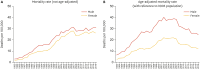
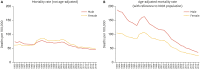
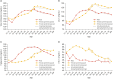
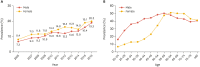
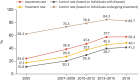

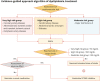
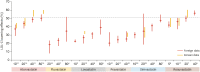

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Health Observatory (GHO) data [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; c2019. [cited 2019 Jun 20]. Available from: http://www.who.int/gho/ncd/mortality_morbidity/ncd_total/en/index.html.
-
- World Health Organization. Preventing chronic diseases: a vital investment [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; c2019. [cited 2019 Jun 20]. Available from: http://www.who.int/chp/chronic_disease_report/en.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

