Randomized Phase II Trial of Nivolumab With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Versus Nivolumab Alone in Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 32822275
- PMCID: PMC8462641
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.20.00290
Randomized Phase II Trial of Nivolumab With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Versus Nivolumab Alone in Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: The objective response rate (ORR) for single-agent anti-programmed death receptor 1 (anti-PD-1) therapy is modest in patients with metastatic or recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). We aimed to test whether radiotherapy may act synergistically with anti-PD-1 therapy to improve response through the abscopal effect.
Patients and methods: We conducted a single-center, randomized, phase II trial of nivolumab (anti-PD-1 therapy) versus nivolumab plus stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) in patients with metastatic HNSCC. Patients had at least two metastatic lesions: one that could be safely irradiated and one measurable by RECIST version 1.1. Patients were randomly assigned (1:1), stratified by human papillomavirus status, to nivolumab (3 mg/kg intravenously every 2 weeks) or nivolumab (same dose) plus SBRT (9 Gy × 3) to 1 lesion. The primary end point was ORR in nonirradiated lesions, which was assessed by RECIST in patients with at least one available set of on-treatment images; safety was assessed in a per-protocol population.
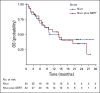
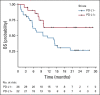
Results: Between March 11, 2016, and June 22, 2018, 62 patients were randomly assigned to nivolumab (n = 30) or nivolumab plus SBRT (n = 32). There was no statistically significant ORR difference between arms (34.5% [95% CI, 19.9% to 52.7%] v 29.0% [95% CI, 16.1% to 46.6%]; P = .86). There was no significant difference in overall survival (P = .75), progression-free survival (P = .79), or response duration (P = .26). Grade 3-5 toxicities were similar (13.3% v 9.7%; P = .70).
Conclusion: We found no improvement in response and no evidence of an abscopal effect with the addition of SBRT to nivolumab in unselected patients with metastatic HNSCC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02684253.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Time to Debunk an Urban Myth? The "Abscopal Effect" With Radiation and Anti-PD-1.J Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan 1;39(1):1-3. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02046. Epub 2020 Sep 28. J Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32986527 No abstract available.
-
Immunotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer-Ready for Prime Time or More Research Needed?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Mar 1;109(3):647-650. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.11.022. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33516431 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Oligometastasis: GUst Do It?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022 Nov 15;114(4):561-570. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2022.07.026. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2022. PMID: 36244387 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C, et al. Pembrolizumab versus methotrexate, docetaxel, or cetuximab for recurrent or metastatic head-and-neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-040): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study Lancet 393156–1672019 - PubMed
-
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 study Lancet 3941915–19282019 - PubMed
-
- Demaria S, Golden EB, Formenti SC.Role of local radiation therapy in cancer immunotherapy JAMA Oncol 11325–13322015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

