Studies of Conorfamide-Sr3 on Human Voltage-Gated Kv1 Potassium Channel Subtypes
- PMID: 32823677
- PMCID: PMC7459591
- DOI: 10.3390/md18080425
Studies of Conorfamide-Sr3 on Human Voltage-Gated Kv1 Potassium Channel Subtypes
Abstract
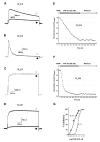
Recently, Conorfamide-Sr3 (CNF-Sr3) was isolated from the venom of Conus spurius and was demonstrated to have an inhibitory concentration-dependent effect on the Shaker K+ channel. The voltage-gated potassium channels play critical functions on cellular signaling, from the regeneration of action potentials in neurons to the regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic cells, among others. In mammals, there are at least 40 genes encoding voltage-gated K+ channels and the process of expression of some of them may include alternative splicing. Given the enormous variety of these channels and the proven use of conotoxins as tools to distinguish different ligand- and voltage-gated ion channels, in this work, we explored the possible effect of CNF-Sr3 on four human voltage-gated K+ channel subtypes homologous to the Shaker channel. CNF-Sr3 showed a 10 times higher affinity for the Kv1.6 subtype with respect to Kv1.3 (IC50 = 2.7 and 24 μM, respectively) and no significant effect on Kv1.4 and Kv1.5 at 10 µM. Thus, CNF-Sr3 might become a novel molecular probe to study diverse aspects of human Kv1.3 and Kv1.6 channels.
Keywords: CNF-Sr3; Conus spurius; FMRFamide peptides; Kv1 voltage-gated K+ channels; Shaker K+ channels; conorfamides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conorfamide-Sr3, a structurally novel specific inhibitor of the Shaker K+ channel.Toxicon. 2017 Nov;138:53-58. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2017.07.024. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Toxicon. 2017. PMID: 28774677
-
Subtype-specific block of voltage-gated K+ channels by μ-conopeptides.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Jan 22;482(4):1135-1140. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.11.170. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 27916464
-
Peptide sr11a from Conus spurius is a novel peptide blocker for Kv1 potassium channels.Peptides. 2010 Jul;31(7):1287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.04.007. Epub 2010 Apr 18. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 20403399
-
Marine Toxins Targeting Kv1 Channels: Pharmacological Tools and Therapeutic Scaffolds.Mar Drugs. 2020 Mar 20;18(3):173. doi: 10.3390/md18030173. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32245015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeras of KcsA and Kv1 as a bioengineering tool to study voltage-gated potassium channels and their ligands.Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;190:114646. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114646. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34090876 Review.
Cited by
-
κO-SrVIA Conopeptide, a Novel Inhibitor Peptide for Two Members of the Human EAG Potassium Channel Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 15;24(14):11513. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411513. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511269 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel Conotoxin Precursors from the Cone Snail Conus spurius by High-Throughput RNA Sequencing.Mar Drugs. 2021 Sep 28;19(10):547. doi: 10.3390/md19100547. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34677446 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide Toxins from Marine Conus Snails with Activity on Potassium Channels and/or Currents.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Nov 22;16(12):504. doi: 10.3390/toxins16120504. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39728762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gene expression profiling of extraocular muscles in primary inferior oblique overaction.PeerJ. 2025 May 28;13:e19474. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19474. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40452936 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

