Enhancement of an In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Oleanolic Acid through Glycosylation Occurring Naturally in Stauntonia hexaphylla
- PMID: 32823787
- PMCID: PMC7464308
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25163699
Enhancement of an In Vivo Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Oleanolic Acid through Glycosylation Occurring Naturally in Stauntonia hexaphylla
Abstract
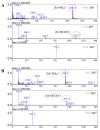
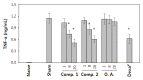
Stauntonia hexaphylla (Lardizabalaceae) has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in Korea and China for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties. As part of a bioprospecting program aimed at the discovery of new bioactive compounds from Korean medicinal plants, a phytochemical study of S. hexaphylla leaves was carried out leading to isolation of two oleanane-type triterpene saponins, 3-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (1→2)-α-l-arabinopyranosyl] oleanolic acid-28-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl] ester (1) and 3-O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl oleanolic acid-28-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl (1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl] ester (2). Their structures were established unambiguously by spectroscopic methods such as one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance and infrared spectroscopies, high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and chemical reactions. Their anti-inflammatory activities were examined for the first time with an animal model for the macrophage-mediated inflammatory response as well as a cell-based assay using an established macrophage cell line (RAW 264.7) in vitro. Together, it was concluded that the saponin constituents, when they were orally administered, exerted much more potent activities in vivo than their sapogenin core even though both the saponins and the sapogenin molecule inhibited the RAW 264.7 cell activation comparably well in vitro. These results imply that saponins from S. hexaphylla leaves have a definite advantage in the development of oral medications for the control of inflammatory responses.
Keywords: Lardizabalaceae; Stauntonia hexaphylla; anti-inflammatory effect; oleanane triterpene saponin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



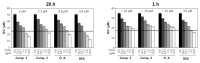
References
-
- Delves P., Martin S., Burton D. Roitt’s Essential Immunology Wiley. 12th ed. Wiley-Blackwell; London, UK: 2011.
-
- Wang C.Y., Lee S., Jang H.-J., Su X.D., Wang H.-S., Kim Y.H., Yang S.Y. Inhibition potential of phenolic constituents from the aerial parts of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum against soluble epoxide hydrolase and nitric oxide synthase. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019;34:753–760. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1584621. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

