Proposal of De Novo Antigen Test for COVID-19: Ultrasensitive Detection of Spike Proteins of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32823866
- PMCID: PMC7459804
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics10080594
Proposal of De Novo Antigen Test for COVID-19: Ultrasensitive Detection of Spike Proteins of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
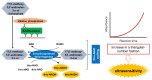
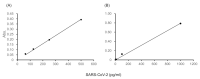
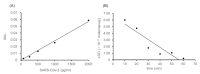
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based antigen tests are technically difficult, time-consuming, and expensive, and may produce false negative results requiring follow-up confirmation with computed tomography. The global coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has increased the demand for accurate, easy-to-use, rapid, and cost-effective antigen tests for clinical application. We propose a de novo antigen test for diagnosing COVID-19 using the combination of sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and thio-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (thio-NAD) cycling. Our test takes advantage of the spike proteins specific to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus. The limit of detection of our test was 2.3 × 10-18 moles/assay. If the virus has ~25 spike proteins on its surface, our method should detect on the order of 10-20 moles of virus/assay, corresponding to ~104 copies of the virus RNA/assay. The detection sensitivity approaches that of PCR-based assays because the average virus RNA load used for PCR-based assays is ~105 copies per oro- or naso-pharyngeal swab specimen. To our knowledge, this is the first ultrasensitive antigen test for SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins that can be performed with an easy-to-use microplate reader. Sufficient sensitivity can be achieved within 10 min of thio-NAD cycling. Our antigen test allows for rapid, cost-effective, specific, ultrasensitive, and simultaneous multiple measurements of SARS-CoV-2, and has broad application for the diagnosis for COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; spike protein; thio-NAD cycling; ultrasensitive ELISA.
Conflict of interest statement
R.T., N.A., K.N., and S.W. are employees of TAUNS Laboratories, Inc. E.I. received research expenses and a patent royalty from TAUNS Laboratories, Inc. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., Baker S.C., Baric R.S., de Groot R.J., Drosten C., Gulyaeva A.A., Haagmans B.L., Lauber C., Leontovich A.M., Neuman B.W., et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020;5:536–544. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Naming the Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) and the Virus that Causes It. [(accessed on 12 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica....
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

