An AC-Rich Bean Element Serves as an Ethylene-Responsive Element in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 32823972
- PMCID: PMC7465537
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9081033
An AC-Rich Bean Element Serves as an Ethylene-Responsive Element in Arabidopsis
Abstract
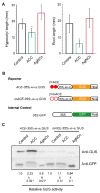
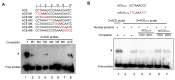
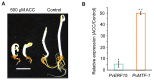
Ethylene-responsive elements (EREs), such as the GCC box, are critical for ethylene-regulated transcription in plants. Our previous work identified a 19-bp AC-rich element (ACE) in the promoter of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) metal response element-binding transcription factor 1 (PvMTF-1). Ethylene response factor 15 (PvERF15) directly binds ACE to enhance PvMTF-1 expression. As a novel ERF-binding element, ACE exhibits a significant difference from the GCC box. Here, we demonstrated that ACE serves as an ERE in Arabidopsis. It conferred the minimal promoter to respond to the ethylene stress and inhibition of ethylene. Moreover, the cis-acting element ACE could specifically bind the nuclear proteins in vitro. We further revealed that the first 9-bp sequence of ACE (ACEcore) is importantly required by the binding of nuclear proteins. In addition, PvERF15 and PvMTF-1 were strongly induced by ethylene in bean seedlings. Since PvERF15 activates PvMTF-1 via ACE, ACE is involved in ethylene-induced PvMTF-1 expression. Taken together, our findings provide genetic and biochemical evidence for a new ERE.
Keywords: AC-rich element; Arabidopsis; ethylene response factor; ethylene-responsive element.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

