Synergistic Effects of Heat-Killed Kefir Paraprobiotics and Flavonoid-Rich Prebiotics on Western Diet-Induced Obesity
- PMID: 32824369
- PMCID: PMC7468817
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12082465
Synergistic Effects of Heat-Killed Kefir Paraprobiotics and Flavonoid-Rich Prebiotics on Western Diet-Induced Obesity
Abstract
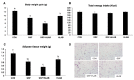
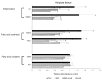
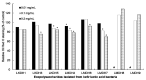
The synergistic anti-obesity effect of paraprobiotic heat-killed lactic acid bacteria (HLAB) and prebiotics has not been studied. To determine the anti-obesity properties of prebiotic polyphenol-rich wine grape seed flour (GSF) and paraprobiotic HLAB, C57BL/6J mice were administered a high-fat and high-fructose diet (HFFrD) with 5% microcrystalline cellulose (CON), HFFrD supplemented with 2.5% GSF, HFFrD with orally administered HLAB, or HFFrD with a combination of GSF and orally administered HLAB (GSF+HLAB) for 8 weeks. Compared with the CON group, the GSF and HLAB groups both showed significant reductions in HFFrD-induced body weight gain and adipose tissue weights (p < 0.05). Interestingly, combined supplementation with GSF and HLAB revealed statistically significant synergistic effects on body weight gain, visceral adiposity, and plasma triacylglycerol concentrations (p < 0.05). The synergistic action was significantly related to a decreased adipocyte gene expression in fatty acid synthesis and inflammation metabolism. In conclusion, the combination of prebiotic GSF and paraprobiotic kefir HLAB is potentially useful, as natural food ingredients, in the prevention of obesity and obesity-related diseases, especially for immunocompromised individuals.
Keywords: heat-killed lactic acid bacteria; obesity; paraprobiotics; prebiotics; wine grape seed flour.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antiobesity Effect of Prebiotic Polyphenol-Rich Grape Seed Flour Supplemented with Probiotic Kefir-Derived Lactic Acid Bacteria.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Nov 28;66(47):12498-12511. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b03720. Epub 2018 Nov 16. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30392364
-
Combination of Whole Grapeseed Flour and Newly Isolated Kefir Lactic Acid Bacteria Reduces High-Fat-Induced Hepatic Steatosis.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019 Feb;63(4):e1801040. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201801040. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2019. PMID: 30537110
-
Effects of kefir lactic acid bacteria-derived postbiotic components on high fat diet-induced gut microbiota and obesity.Food Res Int. 2022 Jul;157:111445. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2022.111445. Epub 2022 May 30. Food Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35761685
-
Potential Prebiotic Properties of Nuts and Edible Seeds and Their Relationship to Obesity.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 3;10(11):1645. doi: 10.3390/nu10111645. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30400274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Oleaster (Elaeagnus angustifolia): A Comprehensive Review on Its Composition, Ethnobotanical and Prebiotic Values>Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021;22(3):367-379. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666191107112243. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 31696816 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiobesity and Antioxidative Effect of Fermented Brown Rice Using In Vitro with In Vivo Caenorhabditis elegans Model.Life (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;13(2):374. doi: 10.3390/life13020374. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836733 Free PMC article.
-
The Biotics Family: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives in Metabolic Diseases.Life (Basel). 2022 Aug 19;12(8):1263. doi: 10.3390/life12081263. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36013442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could paraprobiotics be a safer alternative to probiotics for managing cancer chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicities?Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023 Jan 16;55:e12522. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12522. eCollection 2023. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2023. PMID: 36651453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbiotics against Obesity: Perception and Overview Based on Pre-Clinical and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 29;24(7):6414. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076414. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postbiotics as Metabolites and Their Biotherapeutic Potential.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 16;25(10):5441. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105441. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791478 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

