Characterization of Signal Sequences Determining the Nuclear/Nucleolar Import and Nuclear Export of the Caprine Arthritis-Encephalitis Virus Rev Protein
- PMID: 32824614
- PMCID: PMC7471974
- DOI: 10.3390/v12080900
Characterization of Signal Sequences Determining the Nuclear/Nucleolar Import and Nuclear Export of the Caprine Arthritis-Encephalitis Virus Rev Protein
Abstract
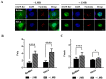
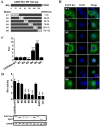
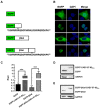
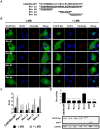
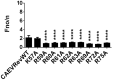
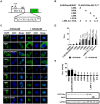
Caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus (CAEV), a lentivirus, relies on the action of the Rev protein for its replication. The CAEV Rev fulfills its function by allowing the nuclear exportation of partially spliced or unspliced viral mRNAs. In this study, we characterized the nuclear and nucleolar localization signals (NLS and NoLS, respectively) and the nuclear export signal (NES) of the CAEV Rev protein. These signals are key actors in the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of a lentiviral Rev protein. Several deletion and alanine substitution mutants were generated from a plasmid encoding the CAEV Rev wild-type protein that was fused to the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). Following cell transfection, images were captured by confocal microscopy and the fluorescence was quantified in the different cell compartments. The results showed that the NLS region is localized between amino acids (aa) 59 to 75, has a monopartite-like structure and is exclusively composed of arginine residues. The NoLS was found to be partially associated with the NLS. Finally, the CAEV Rev protein's NES mapped between aa 89 to 101, with an aa spacing between the hydrophobic residues that was found to be unconventional as compared to that of other retroviral Rev/Rev-like proteins.
Keywords: Rev protein; caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus; nuclear export signal (NES); nuclear localization signal (NLS); nucleolar localization signal (NoLS); small ruminant lentivirus (SRLV).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Jembrana disease virus Rev protein: Identification of nuclear and novel lentiviral nucleolar localization and nuclear export signals.PLoS One. 2019 Aug 22;14(8):e0221505. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221505. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31437223 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the nuclear and nucleolar localization signals of the Feline immunodeficiency virus Rev protein.Virus Res. 2020 Dec;290:198153. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198153. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 33010374
-
The bovine immunodeficiency virus rev protein: identification of a novel lentiviral bipartite nuclear localization signal harboring an atypical spacer sequence.J Virol. 2009 Dec;83(24):12842-53. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01613-09. Epub 2009 Oct 14. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19828621 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar-cytoplasmic shuttling of PRRSV nucleocapsid protein: a simple case of molecular mimicry or the complex regulation by nuclear import, nucleolar localization and nuclear export signal sequences.Virus Res. 2003 Sep;95(1-2):23-33. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1702(03)00161-8. Virus Res. 2003. PMID: 12921993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleocytoplasmic RNA transport in retroviral replication.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2001;34:197-217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-40025-7_12. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2001. PMID: 11288676 Review.
References
-
- Peterhans E., Greenland T., Badiola J., Harkiss G., Bertoni G., Amorena B., Eliaszewicz M., Juste R.A., Krassnig R., Lafont J.P., et al. Routes of transmission and consequences of small ruminant lentiviruses (SRLVs) infection and eradication schemes. Vet. Res. 2004;35:257–274. doi: 10.1051/vetres:2004014. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

