Development of High-Density Genetic Linkage Maps and Identification of Loci for Chestnut Gall Wasp Resistance in Castanea spp
- PMID: 32824716
- PMCID: PMC7465717
- DOI: 10.3390/plants9081048
Development of High-Density Genetic Linkage Maps and Identification of Loci for Chestnut Gall Wasp Resistance in Castanea spp
Abstract
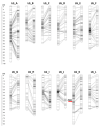
Castanea sativa is an important multipurpose species in Europe for nut and timber production as well as for its role in the landscape and in the forest ecosystem. This species has low tolerance to chestnut gall wasp (Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu), which is a pest that was accidentally introduced into Europe in early 2000 and devastated forest and orchard trees. Resistance to the gall wasp was found in the hybrid cultivar 'Bouche de Bétizac' (C. sativa × C. crenata) and studied by developing genetic linkage maps using a population derived from a cross between 'Bouche de Bétizac' and the susceptible cultivar 'Madonna' (C. sativa). The high-density genetic maps were constructed using double-digest restriction site-associated DNA-seq and simple sequence repeat markers. The map of 'Bouche de Bétizac' consisted of 1459 loci and spanned 809.6 cM; the map of 'Madonna' consisted of 1089 loci and spanned 753.3 cM. In both maps, 12 linkage groups were identified. A single major QTL was recognized on the 'Bouche de Bétizac' map, explaining up to 67-69% of the phenotypic variance of the resistance trait (Rdk1). The Rdk1 quantitative trait loci (QTL) region included 11 scaffolds and two candidate genes putatively involved in the resistance response were identified. This study will contribute to C. sativa breeding programs and to the study of Rdk1 genes.
Keywords: Dryocosmus kuriphilus Yasumatsu; SSR; breeding; chestnut; ddRAD-seq.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bounous G., Marinoni D.T. Chestnut: Botany, Horticulture, and Utilization. Hortic. Rev. 2010;31:291–347. doi: 10.1002/9780470650882.ch6. - DOI
-
- Pereira-Lorenzo S., Ballester A., Corredoira E., Viéitez A.M., Agnanostakis S., Costa R.L., Bounous G., Botta R., Beccaro G.L., Kubisiak T.L., et al. Chestnut. In: Badenes M.L., Byrne D.H., editors. Fruit Breeding. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2012. pp. 729–769.
-
- Torello-Marinoni D., Nishio S., Portis E., Valentini N., Sartor C., Dini F., Ruffa P., Oglietti S., Martino G., Akkak A., et al. Development of a genetic linkage map for molecular breeding of chestnut. Acta Hortic. 2018;1220:23–28. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2018.1220.4. - DOI
-
- Santos C., Nelson C.D., Zhebentyayeva T., Machado H., Gomes-Laranjo J., Costa R.L. First interspecific genetic linkage map for Castanea sativa × Castanea crenata revealed QTLs for resistance to Phytophthora cinnamomi. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0184381. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184381. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santos C., Zhebentyayeva T., Serrazina S., Nelson C.D., Costa R.L. Development and characterization of EST-SSR markers for mapping reaction to Phytophthora cinnamomi in Castanea spp. Sci. Hortic. 2015;194:181–187. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2015.07.043. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

