The Molecular Basis and Biologic Significance of the β-Dystroglycan-Emerin Interaction
- PMID: 32824881
- PMCID: PMC7504044
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21175944
The Molecular Basis and Biologic Significance of the β-Dystroglycan-Emerin Interaction
Abstract
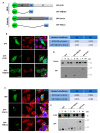
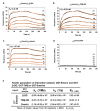
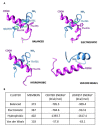
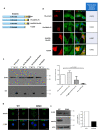
β-dystroglycan (β-DG) assembles with lamins A/C and B1 and emerin at the nuclear envelope (NE) to maintain proper nuclear architecture and function. To provide insight into the nuclear function of β-DG, we characterized the interaction between β-DG and emerin at the molecular level. Emerin is a major NE protein that regulates multiple nuclear processes and whose deficiency results in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD). Using truncated variants of β-DG and emerin, via a series of in vitro and in vivo binding experiments and a tailored computational analysis, we determined that the β-DG-emerin interaction is mediated at least in part by their respective transmembrane domains (TM). Using surface plasmon resonance assays we showed that emerin binds to β-DG with high affinity (KD in the nanomolar range). Remarkably, the analysis of cells in which DG was knocked out demonstrated that loss of β-DG resulted in a decreased emerin stability and impairment of emerin-mediated processes. β-DG and emerin are reciprocally required for their optimal targeting within the NE, as shown by immunofluorescence, western blotting and immunoprecipitation assays using emerin variants with mutations in the TM domain and B-lymphocytes of a patient with EDMD. In summary, we demonstrated that β-DG plays a role as an emerin interacting partner modulating its stability and function.
Keywords: Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy; emerin; nuclear envelope; proteasome; surface plasmon resonance assay; β-dystroglycan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The cell cycle dependent mislocalisation of emerin may contribute to the Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy phenotype.J Cell Sci. 2002 Jan 15;115(Pt 2):341-54. doi: 10.1242/jcs.115.2.341. J Cell Sci. 2002. PMID: 11839786
-
Lmo7 is an emerin-binding protein that regulates the transcription of emerin and many other muscle-relevant genes.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Dec 1;15(23):3459-72. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl423. Epub 2006 Oct 26. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 17067998
-
Distinct functional domains in nesprin-1alpha and nesprin-2beta bind directly to emerin and both interactions are disrupted in X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy.Exp Cell Res. 2007 Aug 1;313(13):2845-57. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.03.025. Epub 2007 Mar 30. Exp Cell Res. 2007. PMID: 17462627
-
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy: focal point nuclear envelope.Curr Opin Neurol. 2019 Oct;32(5):728-734. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000741. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31460960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy at the nuclear envelope: 10 years on.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Dec;63(23):2702-9. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6247-8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 17013557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRF2 interaction with nuclear envelope is required for cell polarization and metastasis in triple negative breast cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Mar 30;16(1):224. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07415-4. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40159489 Free PMC article.
-
From adhesion complex to signaling hub: the dual role of dystroglycan.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Dec 14;10:1325284. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1325284. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38155958 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Emerin in Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 19;22(20):11289. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011289. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of β-Dystroglycan in Nuclear Dynamics.Cells. 2024 Feb 29;13(5):431. doi: 10.3390/cells13050431. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474395 Free PMC article.
-
Natural History of Dilated Cardiomyopathy Due to c.77T>C (p.Val26Ala) in Emerin Protein.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 23;13(3):660. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030660. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martínez-Vieyra I.A., Vásquez-Limeta A., González-Ramírez R., Morales-Lázaro S.L., Mondragón M., Mondragón R., Ortega A., Winder S.J., Cisneros B. A role for β-dystroglycan in the organization and structure of the nucleus in myoblasts. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta. 2013;1833:698–711. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.11.019. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

