In Vitro Modeling of Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema States
- PMID: 32824891
- PMCID: PMC7559923
- DOI: 10.3390/ph13090201
In Vitro Modeling of Bradykinin-Mediated Angioedema States
Abstract
Kinins (peptides related to bradykinin, BK) are formed from circulating substrates, the kininogens, by the action of two proteases, the kallikreins. The only clinical application of a BK receptor ligand, the B2 receptor antagonist icatibant, is the treatment of the rare hereditary angioedema (HAE) caused by the deficiency of C1-esterase inhibitor (C1-INH). Less common forms of HAE (genetic variants of factor XII, plasminogen, kininogen) are presumably mediated by increased BK formation. Acquired forms of BK-mediated angioedema, such as that associated with angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibition, are also known. Antibody-based analytical techniques are briefly reviewed, and support that kinins are extremely short-lived, prominently cleared by ACE. Despite evidence of continuous activation of the kallikrein-kinin system in HAE, patients are not symptomatic most of the time and their blood or plasma obtained during remission does not generate excessive immunoreactive BK (iBK), suggesting effective homeostatic mechanisms. HAE-C1-INH and HAE-FXII plasmas are both hyperresponsive to fibrinolysis activation. On another hand, we suggested a role for the alternate tissue kallikrein-kinin system in patients with a plasminogen mutation. The role of the BK B1 receptor is still uncertain in angioedema states. iBK profiles under in vitro stimulation provide fresh insight into the physiopathology of angioedema.
Keywords: acquired angioedema; analytical techniques for kinins; bradykinin; hereditary angioedema; kallikrein–kinin system.
Conflict of interest statement
F.M. served as a consultant for Pharvaris B.V. and received research funds from Shire/Takeda and Pharvaris B.V. G.E.R. has been a member of advisory boards (Baxalta, Bayer, Biogen Idec, CSL Berhing, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer) and received funding from Bayer, CSL Behring and Pfizer (unrelated to the submitted work). J.H. has been a speaker/teacher for CLS Behring, Novartis, and Shire; he has been a member of advisory committees (CLS Behring, Shire, and Novartis) and a clinical investigator for Merck (ALK), Stallergene, Boehringer-Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Novartis, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, CLS Behring, Shire, Roche, and Griffols (unrelated to the submitted work). The other authors have no conflict of interest to disclose. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

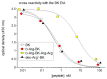

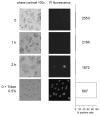

Similar articles
-
Measurement of Bradykinin Formation and Degradation in Blood Plasma: Relevance for Acquired Angioedema Associated With Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibition and for Hereditary Angioedema Due to Factor XII or Plasminogen Gene Variants.Front Med (Lausanne). 2020 Jul 17;7:358. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00358. eCollection 2020. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32766265 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing Pathways of Bradykinin Formation in Whole Blood From Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Hereditary Angioedema Due to C1 Inhibitor Deficiency.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 2;9:2183. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02183. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30333824 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary and acquired C1-inhibitor-dependent angioedema: from pathophysiology to treatment.Ann Med. 2016;48(4):256-67. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2016.1162909. Epub 2016 Mar 26. Ann Med. 2016. PMID: 27018196 Review.
-
C1-inhibitor polymers activate the FXII-dependent kallikrein-kinin system: Implication for a role in hereditary angioedema.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1850(6):1336-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25800206
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of bradykinin mediated diseases: dysregulation of an innate inflammatory pathway.Adv Immunol. 2014;121:41-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00002-7. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24388213 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinins and Their Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Retinal Pathologies.Cells. 2021 Jul 28;10(8):1913. doi: 10.3390/cells10081913. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benefits of Curcumin in the Vasculature: A Therapeutic Candidate for Vascular Remodeling in Arterial Hypertension and Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension?Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 1;13:848867. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.848867. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35530510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Plasminogen Activation System in Angioedema: Novel Insights on the Pathogenesis.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 1;10(3):518. doi: 10.3390/jcm10030518. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33535668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

