Normoxic Tumour Extracellular Vesicles Modulate the Response of Hypoxic Cancer and Stromal Cells to Doxorubicin In Vitro
- PMID: 32824972
- PMCID: PMC7503554
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21175951
Normoxic Tumour Extracellular Vesicles Modulate the Response of Hypoxic Cancer and Stromal Cells to Doxorubicin In Vitro
Abstract
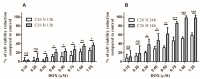
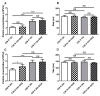
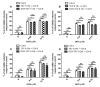
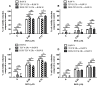
Extracellular vesicles (EV) secreted in the tumour microenvironment (TME) are emerging as major antagonists of anticancer therapies by orchestrating the therapeutic outcome through altering the behaviour of recipient cells. Recent evidence suggested that chemotherapeutic drugs could be responsible for the EV-mediated tumour-stroma crosstalk associated with cancer cell drug resistance. Here, we investigated the capacity of tumour EV (TEV) secreted by normoxic and hypoxic (1% oxygen) C26 cancer cells after doxorubicin (DOX) treatment to alter the response of naïve C26 cells and RAW 264.7 macrophages to DOX. We observed that C26 cells were less responsive to DOX treatment under normoxia compared to hypoxia, and a minimally cytotoxic DOX concentration that mounted distinct effects on cell viability was selected for TEV harvesting. Homotypic and heterotypic pretreatment of naïve hypoxic cancer and macrophage-like cells with normoxic DOX-elicited TEV rendered these cells slightly less responsive to DOX treatment. The observed effects were associated with strong hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) induction and B-cell lymphoma-extra-large anti-apoptotic protein (Bcl-xL)-mediated anti-apoptotic response in normoxic DOX-treated TEV donor cells, being also tightly connected to the DOX-TEV-mediated HIF-1α induction, as well as Bcl-xL levels increasing in recipient cells. Altogether, our results could open new perspectives for investigating the role of chemotherapy-elicited TEV in the colorectal cancer TME and their modulatory actions on promoting drug resistance.
Keywords: colon cancer; doxorubicin; extracellular vesicles; hypoxia; macrophages; normoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

