α-Lactalbumin, Amazing Calcium-Binding Protein
- PMID: 32825311
- PMCID: PMC7565966
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10091210
α-Lactalbumin, Amazing Calcium-Binding Protein
Abstract
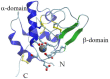
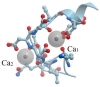
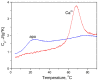
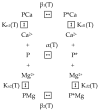
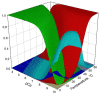
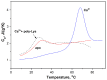
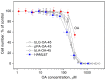
α-Lactalbumin (α-LA) is a small (Mr 14,200), acidic (pI 4-5), Ca2+-binding protein. α-LA is a regulatory component of lactose synthase enzyme system functioning in the lactating mammary gland. The protein possesses a single strong Ca2+-binding site, which can also bind Mg2+, Mn2+, Na+, K+, and some other metal cations. It contains several distinct Zn2+-binding sites. Physical properties of α-LA strongly depend on the occupation of its metal binding sites by metal ions. In the absence of bound metal ions, α-LA is in the molten globule-like state. The binding of metal ions, and especially of Ca2+, increases stability of α-LA against the action of heat, various denaturing agents and proteases, while the binding of Zn2+ to the Ca2+-loaded protein decreases its stability and causes its aggregation. At pH 2, the protein is in the classical molten globule state. α-LA can associate with membranes at neutral or slightly acidic pH at physiological temperatures. Depending on external conditions, α-LA can form amyloid fibrils, amorphous aggregates, nanoparticles, and nanotubes. Some of these aggregated states of α-LA can be used in practical applications such as drug delivery to tissues and organs. α-LA and some of its fragments possess bactericidal and antiviral activities. Complexes of partially unfolded α-LA with oleic acid are cytotoxic to various tumor and bacterial cells. α-LA in the cytotoxic complexes plays a role of a delivery carrier of cytotoxic fatty acid molecules into tumor and bacterial cells across the cell membrane. Perhaps in the future the complexes of α-LA with oleic acid will be used for development of new anti-cancer drugs.
Keywords: amyloid fibrils; cytotoxicity; folding; liprotides; metal binding; molten globule; nanoparticles; nanotubes; structure; unfolding; α-lactalbumin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
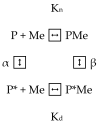
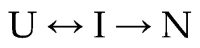
References
-
- Renner E. Milk and Dairy Products in Human Nutrition. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 1983. Milk and dairy products in human nutrition.
-
- Montagne P., Cuilliere M.L., Mole C., Bene M.C., Faure G. Immunological and nutritional composition of human milk in relation to prematurity and mother’s parity during the first 2 weeks of lactation. J. Pediatric Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1999;29:75–80. doi: 10.1097/00005176-199907000-00018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hill R.L., Brew K. Lactose synthetase. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Areas Mol. Biol. 1975;43:411–490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

