A Comprehensive Review on Optical Properties of Polymer Electrolytes and Composites
- PMID: 32825367
- PMCID: PMC7503865
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13173675
A Comprehensive Review on Optical Properties of Polymer Electrolytes and Composites
Abstract
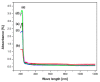
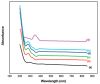
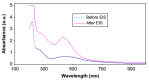
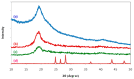
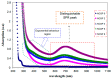
Polymer electrolytes and composites have prevailed in the high performance and mobile marketplace during recent years. Polymer-based solid electrolytes possess the benefits of low flammability, excellent flexibility, good thermal stability, as well as higher safety. Several researchers have paid attention to the optical properties of polymer electrolytes and their composites. In the present review paper, first, the characteristics, fundamentals, advantages and principles of various types of polymer electrolytes were discussed. Afterward, the characteristics and performance of various polymer hosts on the basis of specific essential and newly published works were described. New developments in various approaches to investigate the optical properties of polymer electrolytes were emphasized. The last part of the review devoted to the optical band gap study using two methods: Tauc's model and optical dielectric loss parameter. Based on recently published literature sufficient quantum mechanical backgrounds were provided to support the applicability of the optical dielectric loss parameter for the band gap study. In this review paper, it was demonstrated that both Tauc's model and optical dielectric loss should be studied to specify the type of electron transition and estimate the optical band gap accurately. Other parameters such as absorption coefficient, refractive index and optical dielectric constant were also explored.
Keywords: nanocomposite; optical dielectric loss; optical properties; polymer composite; polymer electrolyte; taucs model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




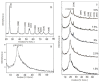
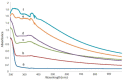
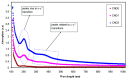
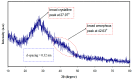

References
-
- Fenton D.E., Parker J.M., Wright P.V. Complexes of alkali metal ions with poly(ethylene oxide) Polymer. 1973;14:589. doi: 10.1016/0032-3861(73)90146-8. - DOI
-
- Bruce P.G. Solid State Electrochemistry. 1st ed. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 1995. - DOI
-
- Hamsan M.H., Shukur M.F., Aziz S.B., Yusof Y.M., Kadir M.F.Z. Influence of NH4Br as an ionic source on the structural/electrical properties of dextran-based biopolymer electrolytes and EDLC application. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019;43 doi: 10.1007/s12034-019-2008-9. - DOI
-
- Aziz S.B., Brza M.A., Hamsan M.H., Kadir M.F.Z., Muzakir S.K., Abdulwahid R.T. Effect of ohmic-drop on electrochemical performance of EDLC fabricated from PVA:Dextran:NH4I based polymer blend electrolytes. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.01.110. - DOI
-
- Hamsan M.H., Aziz S.B., Azha M.A.S., Azli A.A., Shukur M.F., Yusof Y.M., Muzakir S.K., Manan N.S.A., Kadir M.F.Z. Solid-state double layer capacitors and protonic cell fabricated with dextran from Leuconostoc mesenteroides based green polymer electrolyte. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020;241 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122290. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

