Physical Activity Counseling for Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial
- PMID: 32825535
- PMCID: PMC7503854
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17176076
Physical Activity Counseling for Adults with Hypertension: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial
Abstract
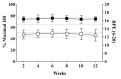
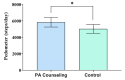
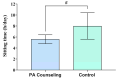
The effect of physical activity counseling (PAC) in hypertensive adults is unclear. This study investigated the effect of PAC on blood pressure (BP), physical activity level, sitting time, metabolic profile, and body composition in hypertensive adults. Twenty-two hypertensive adults (48.8 ± 7.3 years) participated in this pilot trial. The 12-week PAC was based on the 5 A's model considering the FITT principle (Frequency, Intensity, Time, and Type) of physical activity. The control group received instructions about FITT in one face-to-face meeting at baseline. Pedometer-measured physical activity, sitting time, resting and ambulatory BP, metabolic profile (cholesterol, triglycerides, fasting glucose), and body composition (fat mass, abdominal fat, fat free mass) were assessed. The PAC group showed higher steps per day (5839 ± 992 vs. 5028 ± 902; p = 0.044) and a trend for lower sitting time (5.6 ± 1.3 vs. 8.0 ± 4.0 h/day; p = 0.059) than the control group. No changes were observed in BP, metabolic profile, and body composition (p > 0.05). In conclusion, 12 weeks of a PAC program based on the 5 A's model resulted in a modest increase of ~800 steps per day and a trend to decrease ~2 h/day in sitting time, but there were no associated reduction in BP and improvements in metabolic and body composition.
Keywords: cardiovascular health; exercise; health behavior; pedometry; sitting/standing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . World Health Organization. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. A global brief on hypertension: Silent killet, global public health crisis: World Health Day 2013; pp. 1–40.
-
- Daskalopoulou S.S., Rabi D.M., Zarnke K.B., Dasgupta K., Nerenberg K., Cloutier L., Gelfer M., Lamarre-Cliche M., Milot A., Bolli P., et al. The 2015 Canadian Hypertension Education Program Recommendations for Blood Pressure Measurement, Diagnosis, Assessment of Risk, Prevention, and Treatment of Hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2015;31:549–568. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2015.02.016. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

