Leveraging Neural Networks in Preclinical Alcohol Research
- PMID: 32825739
- PMCID: PMC7565429
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10090578
Leveraging Neural Networks in Preclinical Alcohol Research
Abstract
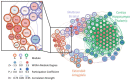
Alcohol use disorder is a pervasive healthcare issue with significant socioeconomic consequences. There is a plethora of neural imaging techniques available at the clinical and preclinical level, including magnetic resonance imaging and three-dimensional (3D) tissue imaging techniques. Network-based approaches can be applied to imaging data to create neural networks that model the functional and structural connectivity of the brain. These networks can be used to changes to brain-wide neural signaling caused by brain states associated with alcohol use. Neural networks can be further used to identify key brain regions or neural "hubs" involved in alcohol drinking. Here, we briefly review the current imaging and neurocircuit manipulation methods. Then, we discuss clinical and preclinical studies using network-based approaches related to substance use disorders and alcohol drinking. Finally, we discuss how preclinical 3D imaging in combination with network approaches can be applied alone and in combination with other approaches to better understand alcohol drinking.
Keywords: addiction; alcohol use disorder; animal model; binge drinking; dependence; fMRI; graph theory; iDISCO; modularity; substance use disorder.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- SAMHSA Samhsa Alcohol Use Disorder in the Past Year, by Age Group and State: Percentages, Annual Averages Based on 2014 and 2015 NSDUHs. [(accessed on 12 July 2020)]; Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov.
-
- Koob G.F., Ahmed S.H., Boutrel B., Chen S.A., Kenny P.J., Markou A., O’dell L.E., Parsons L.H., Sanna P.P. Neurobiological mechanisms in the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004;27:739–749. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

