Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate
- PMID: 32826322
- PMCID: PMC7587101
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02107-20
Neutralizing Antibodies Correlate with Protection from SARS-CoV-2 in Humans during a Fishery Vessel Outbreak with a High Attack Rate
Abstract
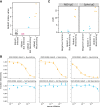
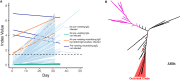
The development of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 would be greatly facilitated by the identification of immunological correlates of protection in humans. However, to date, studies on protective immunity have been performed only in animal models and correlates of protection have not been established in humans. Here, we describe an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 on a fishing vessel associated with a high attack rate. Predeparture serological and viral reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) testing along with repeat testing after return to shore was available for 120 of the 122 persons on board over a median follow-up of 32.5 days (range, 18.8 to 50.5 days). A total of 104 individuals had an RT-PCR-positive viral test with a cycle threshold (CT ) of <35 or seroconverted during the follow-up period, yielding an attack rate on board of 85.2% (104/122 individuals). Metagenomic sequencing of 39 viral genomes suggested that the outbreak originated largely from a single viral clade. Only three crew members tested seropositive prior to the boat's departure in initial serological screening and also had neutralizing and spike-reactive antibodies in follow-up assays. None of the crew members with neutralizing antibody titers showed evidence of bona fide viral infection or experienced any symptoms during the viral outbreak. Therefore, the presence of neutralizing antibodies from prior infection was significantly associated with protection against reinfection (Fisher's exact test, P = 0.002).
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; attack rate; boat; correlates; fishing; neutralizing antibodies; protection; vessel.
Copyright © 2020 Addetia et al.
Figures
Update of
-
Neutralizing antibodies correlate with protection from SARS-CoV-2 in humans during a fishery vessel outbreak with high attack rate.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 Aug 14:2020.08.13.20173161. doi: 10.1101/2020.08.13.20173161. medRxiv. 2020. Update in: J Clin Microbiol. 2020 Oct 21;58(11):e02107-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02107-20. PMID: 32817980 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Corbett KS, Flynn B, Foulds KE, Francica JR, Boyoglu-Barnum S, Werner AP, Flach B, O’Connell S, Bock KW, Minai M, Nagata BM, Andersen H, Martinez DR, Noe AT, Douek N, Donaldson MM, Nji NN, Alvarado GS, Edwards DK, Flebbe DR, Lamb E, Doria-Rose NA, Lin BC, Louder MK, O’Dell S, Schmidt SD, Phung E, Chang LA, Yap C, Todd J-PM, Pessaint L, Van Ry A, Browne S, Greenhouse J, Putman-Taylor T, Strasbaugh A, Campbell T-A, Cook A, Dodson A, Steingrebe K, Shi W, Zhang Y, Abiona OM, Wang L, Pegu A, Yang ES, Leung K, Zhou T, Teng I-T, Widge A, et al. 28 July 2020. Evaluation of the mRNA-1273 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 in nonhuman primates. N Engl J Med doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024671. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Doremalen N, Lambe T, Spencer A, Belij-Rammerstorfer S, Purushotham JN, Port JR, Avanzato VA, Bushmaker T, Flaxman A, Ulaszewska M, Feldmann F, Allen ER, Sharpe H, Schulz J, Holbrook M, Okumura A, Meade-White K, Pérez-Pérez L, Edwards NJ, Wright D, Bissett C, Gilbride C, Williamson BN, Rosenke R, Long D, Ishwarbhai A, Kailath R, Rose L, Morris S, Powers C, Lovaglio J, Hanley PW, Scott D, Saturday G, de Wit E, Gilbert SC, Munster VJ. 30 July 2020. ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine prevents SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in rhesus macaques. Nature doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2608-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gao Q, Bao L, Mao H, Wang L, Xu K, Yang M, Li Y, Zhu L, Wang N, Lv Z, Gao H, Ge X, Kan B, Hu Y, Liu J, Cai F, Jiang D, Yin Y, Qin C, Li J, Gong X, Lou X, Shi W, Wu D, Zhang H, Zhu L, Deng W, Li Y, Lu J, Li C, Wang X, Yin W, Zhang Y, Qin C. 2020. Development of an inactivated vaccine candidate for SARS-CoV-2. Science 369:77–81. doi: 10.1126/science.abc1932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ju B, Zhang Q, Ge J, Wang R, Sun J, Ge X, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou B, Song S, Tang X, Yu J, Lan J, Yuan J, Wang H, Zhao J, Zhang S, Wang Y, Shi X, Liu L, Zhao J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhang L. 2020. Human neutralizing antibodies elicited by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nature 584:115–119. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2380-z. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

