Propofol-induced MiR-20b expression initiates endogenous cellular signal changes mitigating hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagy in vitro
- PMID: 32826852
- PMCID: PMC7442825
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02828-9
Propofol-induced MiR-20b expression initiates endogenous cellular signal changes mitigating hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagy in vitro
Abstract
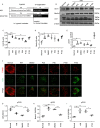
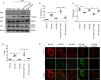
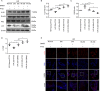
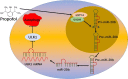
Certain miRNAs can attenuate hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced autophagic cell death reported in our previous studies, but how these miRNAs regulate the autophagy-related cellular signaling pathway in preventing cell death is largely unknown. In the current study, the autophagy-related miRNAs of hsa-miR-20b were investigated in an in vitro model of hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagic cell death. Of these, miR-20b was found to be the most important miRNA which targeted on the key autophagy kinase ULK1 and inhibited hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury-induced autophagy by decreasing both autophagosomes and LC3I to II transition rate and P62 degradation. These processes were reversed by the transfection of an miR-20b inhibitor. Re-expression of ULK1 restores miR-20b-inhibited autophagy. Propofol, a commonly used anesthetic, promoted miR-20b and METTL3 expression and attenuated endothelial autophagic cell death. The inhibited endogenous expression of miR-20b or silenced METTL3 diminished the protective effect of propofol and accentuated autophagy. Additionally, METTL3 knockdown significantly inhibited miR-20b expression but up-regulated pri-miR-20b expression. Together, our data shows that propofol protects against endothelial autophagic cell death induced by hypoxia/re-oxygenation injury, associated with activation of METTL3/miR-20b/ULK1 cellular signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-20b-5p regulates propofol-preconditioning-induced inhibition of autophagy in hypoxia-and-reoxygenation-stimulated endothelial cells.J Biosci. 2020;45:35. J Biosci. 2020. PMID: 32098914
-
Differential microRNA profiling in a cellular hypoxia reoxygenation model upon posthypoxic propofol treatment reveals alterations in autophagy signaling network.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:378484. doi: 10.1155/2013/378484. Epub 2013 Dec 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 24454982 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-93 Regulates Hypoxia-Induced Autophagy by Targeting ULK1.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:2709053. doi: 10.1155/2017/2709053. Epub 2017 Oct 3. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29109831 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of miR-21/exosomal miR-21 in autophagy pathway.Pathol Res Pract. 2024 May;257:155275. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155275. Epub 2024 Mar 30. Pathol Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 38643552 Review.
-
Crucial role of autophagy in propofol-treated neurological diseases: a comprehensive review.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Oct 25;17:1274727. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1274727. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37946715 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The dual role of microRNA (miR)-20b in cancers: Friend or foe?Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 30;21(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01019-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36717861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks regulating oxygen utilization in type II alveolar epithelial cells of Tibetan pigs.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 21;9:854250. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.854250. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36213124 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insights into vascular biology via methyltransferase-like 3-driven N6-adenosine methylation of RNA.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jan 6;12:1482753. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1482753. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 39834386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights into The Roles of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification and Autophagy in Human Diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jan 1;19(2):705-720. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.75466. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36632456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating levels of miR-20b-5p are associated with survival in cardiogenic shock.J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025 Jan 17;11:100284. doi: 10.1016/j.jmccpl.2025.100284. eCollection 2025 Mar. J Mol Cell Cardiol Plus. 2025. PMID: 39927096 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hughes SF, Cotter MJ, Evans SA, Jones KP, Adams RA. Role of leucocytes in damage to the vascular endothelium during ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006;63:166–170. - PubMed
-
- Kokura S, Yoshida N, Yoshikawa T. Anoxia/reoxygenation-induced leukocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2002;33:427–432. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

