ALV-J inhibits autophagy through the GADD45β/MEKK4/P38MAPK signaling pathway and mediates apoptosis following autophagy
- PMID: 32826872
- PMCID: PMC7442830
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-020-02841-y
ALV-J inhibits autophagy through the GADD45β/MEKK4/P38MAPK signaling pathway and mediates apoptosis following autophagy
Abstract
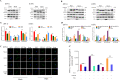
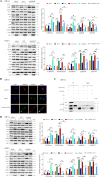
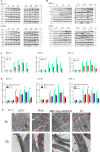
Autophagy and apoptosis, which are important processes for host immunity, are commonly exploited by viruses to facilitate their survival. However, to the best of our knowledge, very few studies have researched the mechanisms of action of the autophagic and apoptotic signaling pathways following viral infection. Thus, the present study aimed to investigate the mechanisms of action of growth arrest and DNA-damage-inducible β (GADD45β), an important resistance gene involved in the host resistance to ALV-J. Both ALV-J infection and the overexpression of GADD45β inhibited autophagy during the early stages, which prevented the autophagosomes from binding to the lysosomes and resulted in an incomplete autophagic flux. Notably, GADD45β was discovered to interact with MEKK4 in DF-1 cells. The genetic knockdown of GADD45β and MEKK4 using small interfering RNA-affected ALV-J infection, which suggested that ALV-J may promote the binding of GADD45β to MEKK4 to activate the p38MAPK signaling pathway, which subsequently inhibits autophagy. Furthermore, ALV-J was revealed to affect the autophagic pathway prior to affecting the apoptotic pathway. In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, the present study was the first to investigate the combined effects of ALV-J infection on autophagy and apoptosis, and to suggest that ALV-J inhibits autophagy via the GADD45β/MEKK4/p38MAPK signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of Atg5 by the Gadd45β-MEKK4-p38 pathway inhibits autophagy.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Feb;20(2):321-32. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.129. Epub 2012 Oct 12. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23059785 Free PMC article.
-
GADD45beta/GADD45gamma and MEKK4 comprise a genetic pathway mediating STAT4-independent IFNgamma production in T cells.EMBO J. 2004 Apr 7;23(7):1576-86. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600173. Epub 2004 Mar 25. EMBO J. 2004. PMID: 15044949 Free PMC article.
-
GADD45β, an anti-tumor gene, inhibits avian leukosis virus subgroup J replication in chickens.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):68883-68893. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12027. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27655697 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of key genes fluctuated induced by avian leukemia virus (ALV-J) infection in chicken cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018 Jan;54(1):41-51. doi: 10.1007/s11626-017-0198-2. Epub 2017 Dec 1. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2018. PMID: 29197030
-
Subgroup J avian leukosis virus infection inhibits autophagy in DF-1 cells.Virol J. 2013 Jun 17;10:196. doi: 10.1186/1743-422X-10-196. Virol J. 2013. PMID: 23773913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of apolipoprotein O in autophagy via the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in myocardial infarction.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022 May 16;77:100046. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100046. eCollection 2022. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022. PMID: 35588578 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin Alleviated AFM1-Induced Apoptosis in Intestinal NCM 460 Cells through the Autophagy Pathway.Foods. 2021 Dec 23;11(1):23. doi: 10.3390/foods11010023. Foods. 2021. PMID: 35010149 Free PMC article.
-
PMAIP1 promotes J subgroup avian leukosis virus replication by regulating mitochondrial function.Poult Sci. 2024 Jun;103(6):103617. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103617. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38547674 Free PMC article.
-
ACSL1 Inhibits ALV-J Replication by IFN-Ⅰ Signaling and PI3K/Akt Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 29;12:774323. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.774323. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34777393 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the role of the GADD45 family in neurodevelopmental, neurodegenerative, and neuropsychiatric disorders.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 25;18:1349409. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1349409. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38332860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gabryel B, Kost A, Kasprowska D. Neuronal autophagy in cerebral ischemia-a potential target for neuroprotective strategies? Pharmacol. Rep. 2012;64:1–15. - PubMed
-
- Erlich S, et al. Differential interactions between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2 family members. Autophagy. 2007;3:561–568. - PubMed
-
- Pyo JO, et al. Essential roles of Atg5 and FADD in autophagic cell death: dissection of autophagic cell death into vacuole formation and cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:20722–20729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

