The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics
- PMID: 32826966
- PMCID: PMC7581511
- DOI: 10.1038/s41575-020-0344-2
The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of synbiotics
Abstract
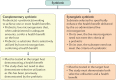
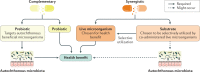
In May 2019, the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) convened a panel of nutritionists, physiologists and microbiologists to review the definition and scope of synbiotics. The panel updated the definition of a synbiotic to "a mixture comprising live microorganisms and substrate(s) selectively utilized by host microorganisms that confers a health benefit on the host". The panel concluded that defining synbiotics as simply a mixture of probiotics and prebiotics could suppress the innovation of synbiotics that are designed to function cooperatively. Requiring that each component must meet the evidence and dose requirements for probiotics and prebiotics individually could also present an obstacle. Rather, the panel clarified that a complementary synbiotic, which has not been designed so that its component parts function cooperatively, must be composed of a probiotic plus a prebiotic, whereas a synergistic synbiotic does not need to be so. A synergistic synbiotic is a synbiotic for which the substrate is designed to be selectively utilized by the co-administered microorganisms. This Consensus Statement further explores the levels of evidence (existing and required), safety, effects upon targets and implications for stakeholders of the synbiotic concept.
Conflict of interest statement
K.S.S. has received funding from Ingredion, Beneo GmbH and Gnubiotics Sciences. G.R.G. currently receives research funding from GlaxoSmithKline, Pukka Herbs, and consulted for Clasado and Pepsico. G.R. has consulted for Seed, KGK Science, Acerus Pharmaceuticals, Danone, Chris Hansen, Altmann, Kimberly Clark and Metagenics. R.H. has received grants or honoraria from Mead Johnson Nutrition, Pharmavite, Danone, Beachbody, and PepsiCo and is a co-owner of Synbiotic Health. R.A.R. has received presentation honoraria from Beneo and research funding from General Mills and Sensus. K.V. received presentation honoraria from Beneo and Yakult, consultancy fees from Comet Bio and research funding from Nestlé. K.P.S. currently receives research funding from Probi and has received presentation honoraria from Yakult. H.D.H. has received presentation honoraria from Kellogg’s, PepsiCo and Nutricia North America. M.B.A. has received grants and presentation honoraria from Prolacta Biosciences and presentation honoraria from Medela. M.E.S. has been compensated for consulting, serving on advisory boards or for speaking engagements from California Dairy Research Foundation, Church & Dwight, Clorox, Danone North America, Danone Research, General Mills, Georgetown, GlaxoSmithKline, International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics, JHeimbach LLC, Kellogg, Kerry, Mead Johnson, PepsiCo, Probi, Trouw, Visalia Dairy Company, Winclove, Yakult and Yakult Foundation of India. N.M.D. declares no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Coyte KZ, Schluter J, Foster KR. The ecology of the microbiome: networks, competition, and stability. Science. 2015;350:663–666. - PubMed
-
- Walker AW, Lawley TD. Therapeutic modulation of intestinal dysbiosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2013;69:75–86. - PubMed
-
- Gibson GR, Roberfroid MB. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995;125:1401–1412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

