Efficacy of Once-Weekly Semaglutide vs Empagliflozin Added to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes: Patient-Level Meta-analysis
- PMID: 32827435
- PMCID: PMC7549924
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa577
Efficacy of Once-Weekly Semaglutide vs Empagliflozin Added to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes: Patient-Level Meta-analysis
Abstract
Context: No head-to-head trials have directly compared once-weekly (OW) semaglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, with empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Objective: We indirectly compared the efficacy of OW semaglutide 1 mg vs once-daily (OD) empagliflozin 25 mg in patients with T2D inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy, using individual patient data (IPD) and meta-regression methodology.
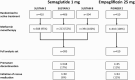
Design, setting, participants, and interventions: IPD for patients with T2D receiving metformin monotherapy and randomized to OW semaglutide 1 mg (SUSTAIN 2, 3, 8 trials), or to OD empagliflozin 25 mg (PIONEER 2 trial) were included. Meta-regression analyses were adjusted for potential prognostic factors and effect modifiers.
Main outcome measures: The primary efficacy outcomes were change from baseline to end-of-treatment (~1 year) in HbA1c (%-point) and body weight (kg). Responder outcomes and other clinically relevant efficacy measures were analyzed.
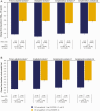
Results: Baseline characteristics were similar between OW semaglutide (n = 995) and empagliflozin (n = 410). Our analyses showed that OW semaglutide significantly reduced mean HbA1c and body weight vs empagliflozin (estimated treatment difference: -0.61%-point [95% confidence interval (CI): -0.72; -0.49] and -1.65 kg [95% CI: -2.22; -1.08], respectively; both P < 0.0001). Complementary analyses supported the robustness of these results. A significantly greater proportion of patients on OW semaglutide vs empagliflozin also achieved HbA1c targets and weight-loss responses.
Conclusions: This indirect comparison suggests that OW semaglutide 1 mg provides superior reductions in HbA1c and body weight vs OD empagliflozin 25 mg in patients with T2D when added to metformin monotherapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01930188 NCT01885208 NCT03136484 NCT02863328.
Keywords: GLP-1 receptor agonist; SGLT-2 inhibitor; indirect comparison; individual patient data; type 2 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes–2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S90-S102. - PubMed
-
- Cosentino F, Grant PJ, Aboyans V, et al. ; ESC Scientific Document Group . 2019 ESC Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases developed in collaboration with the EASD. Eur Heart J. 2020;41(2):255-323. - PubMed
-
- Invokana (canagliflozin tablets) prescribing information. Accessed September 21, 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2016/204042s011lbl.pdf
-
- Farxiga (dapagliflozin tablets) prescribing information. Accessed September 21, 2020. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2014/202293s000lbl.pdf

