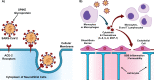
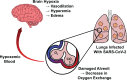
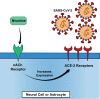
COVID-19 and the central nervous system
- PMID: 32828027
- PMCID: PMC7402113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106116
COVID-19 and the central nervous system
Keywords: Awareness; COVID-19; Encephalopathy; Nervous system; Smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Comment in
-
Possible immunity, inflammation, and oxidative stress mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease in COVID-19 patients.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021 Feb;201:106414. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106414. Epub 2020 Dec 5. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 33341456 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The neurological impact of COVID-19.Lancet Neurol. 2020 Jun;19(6):471. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30142-3. Epub 2020 May 26. Lancet Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32470408 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A call from the European Academy of Neurology on COVID-19.Lancet Neurol. 2020 Jun;19(6):482. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30151-4. Epub 2020 May 26. Lancet Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32470415 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A call for a global COVID-19 Neuro Research Coalition.Lancet Neurol. 2020 Jun;19(6):482-484. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30150-2. Epub 2020 May 26. Lancet Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32470416 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Dyspneic and non-dyspneic (silent) hypoxemia in COVID-19: Possible neurological mechanism.Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020 Nov;198:106217. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106217. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2020. PMID: 32947193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Society of NeuroInterventional Surgery recommendations for the care of emergent neurointerventional patients in the setting of COVID-19.J Neurointerv Surg. 2020 Jun;12(6):539-541. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2020-016098. Epub 2020 Apr 15. J Neurointerv Surg. 2020. PMID: 32295835 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and safety of Qi and Blood Tonic Chinese Medicines in the treatment of COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e32136. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032136. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626419 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Long-Term Outcomes: Lessons from Other Critical Care Illnesses and Potential Mechanisms.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Sep;67(3):275-283. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0374PS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35348443 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular therapeutics: A new potential for anxiety treatment?Med Res Rev. 2022 May;42(3):1202-1245. doi: 10.1002/med.21875. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Med Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 34993995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 neuropsychiatric repercussions: Current evidence on the subject.World J Methodol. 2022 Sep 20;12(5):365-380. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i5.365. eCollection 2022 Sep 20. World J Methodol. 2022. PMID: 36186752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment modalities of facial nerve palsy in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review.Acta Neurol Belg. 2022 Dec;122(6):1419-1432. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-02026-8. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Acta Neurol Belg. 2022. PMID: 35917018 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ma K., et al. [Management and clinical thinking of Coronavirus Disease 2019] Zhonghua gan zang bing za zhi = Zhonghua ganzangbing zazhi = Chinese journal of hepatology. 2020;28(0):E002. - PubMed
-
- WHO . 2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak.
-
- Gorbalenya A.E., et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus</em>: the species and its viruses – a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group. bioRxiv. 2020 p. 2020.02.07.937862.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources