HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 32829253
- PMCID: PMC7452120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101671
HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
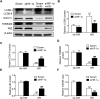
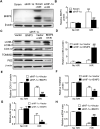
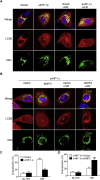
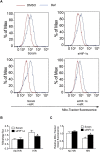
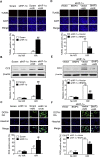
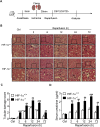
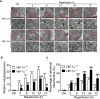
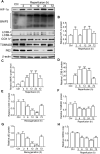
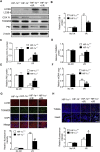
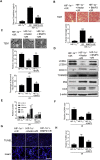
In the present study, we hypothesized that hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α)-mediated mitophagy plays a protective role in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI). Mitophagy was evaluated by measuring the changes of mitophagy flux, mitochondria DNA copy number, and the changes of mitophagy-related proteins including translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 20 (TOMM20), cytochrome c oxidase IV (COX IV), microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3B (LC3B), and mitochondria adaptor nucleoporin p62 in HK2 cells, a human tubular cell line. Results show that HIF-1α knockout significantly attenuated hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R)-induced mitophagy, aggravated H/R-induced apoptosis, and increased the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Similarly, H/R induced significantly increase in Bcl-2 19-kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), a downstream regulator of HIF-1α. Notably, BNIP3 overexpression reversed the inhibitory effect of HIF-1α knockout on H/R-induced mitophagy, and prevented the enhancing effect of HIF-1α knockout on H/R-induced apoptosis and ROS production. For in vivo study, we established HIF-1αflox/flox; cadherin-16-cre mice in which tubular HIF-1α was specifically knockout. It was found that tubular HIF-1α knockout significantly inhibited I/R-induced mitophagy, and aggravated I/R-induced tubular apoptosis and kidney damage. In contrast, adenovirus-mediated BNIP3 overexpression significantly reversed the decreased mitophagy, and prevented enhanced kidney damage in tubular HIF-1α knockout mice with I/R injury. In summary, our study demonstrated that HIF-1α-BNIP3-mediated mitophagy in tubular cells plays a protective role through inhibition of apoptosis and ROS production in acute kidney damage.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Bcl-2 19-kDa interacting protein 3; Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α; Mitophagy; Tubular cells.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Bellomo R., Kellum J.A., Ronco C. Acute kidney injury. Lancet. 2012;380(9843):756–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

