Treatment of Refractory Hypertension with Timely Angioplasty in Total Renal Artery Occlusion with Atrophic Kidney
- PMID: 32830180
- PMCID: PMC7872794
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5290-20
Treatment of Refractory Hypertension with Timely Angioplasty in Total Renal Artery Occlusion with Atrophic Kidney
Abstract
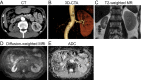
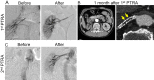
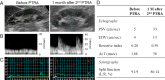
Angioplasty for cases of chronic total occlusion of renal artery with/without atrophic kidney is generally not recommended. We herein report a 57-year-old man who presented with renin-mediated refractory hypertension caused by occlusion of a unilateral renal artery leading to kidney atrophy (length: 69 mm). Angioplasty favorably achieved blood pressure control with normalized renin secretion and enlargement of the atrophic kidney to 85 mm. Timely angioplasty can be beneficial in select patients, even with an atrophic kidney and total occlusion, especially in cases with deterioration of hypertension within six months and the presence of collateral perfusion to the affected kidney.
Keywords: atherosclerotic renovascular disease; diffusion-weighted MRI; renal artery stenosis; renin-angiotensin system inhibitors; renovascular hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Successful percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for the treatment of renovascular hypertension with an atrophic kidney.Heart Vessels. 2015 Mar;30(2):274-9. doi: 10.1007/s00380-013-0457-4. Epub 2014 Jan 3. Heart Vessels. 2015. PMID: 24384893 Free PMC article.
-
Exaggerated natriuresis after renal artery balloon angioplasty for flash pulmonary oedema: a potential complication in one-kidney renovascular hypertension.J Hypertens. 2022 May 1;40(5):1042-1049. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003128. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35249965
-
Treatment of severe hypertension in a 14-year-old child: Successful blood pressure control with additive administration of captopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, in a patient with bilateral renovascular hypertension.Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017;39(7):587-591. doi: 10.1080/10641963.2017.1299747. Epub 2017 Jun 16. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2017. PMID: 28621587
-
Renovascular hypertension following renal transplantation.Urol Clin North Am. 1984 Aug;11(3):491-502. Urol Clin North Am. 1984. PMID: 6235661 Review.
-
New Insights Into Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Renovascular Hypertension.Iran J Kidney Dis. 2017 Mar;11(2):79-89. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28270639 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Endovascular Treatment of Chronic Atherosclerotic Renal Artery Total Occlusions with Failed Medical Therapy.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 18;9:843568. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.843568. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36329980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Investigators A, Wheatley K, Ives N, et al. . Revascularization versus medical therapy for renal-artery stenosis. N Engl J Med 361: 1953-1962, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. . 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 71: e13-e115, 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

