A Rare Cause of Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia: Kabuki Syndrome
- PMID: 32830475
- PMCID: PMC8638635
- DOI: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2020.2020.0065
A Rare Cause of Hyperinsulinemic Hypoglycemia: Kabuki Syndrome
Abstract
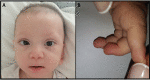
Kabuki syndrome (KS) is a disease characterized by distinctive facial features, skeletal anomalies and delay in neuromotor development. KS 1 is an autosomal dominant condition caused by mutations in the KMT2D gene, whereas KS 2 is an X-linked disorder caused by mutations in the KDM6A gene. In the majority of KS patients who present with hypoglycemia, KDM6A is the defective gene. A 9-month old girl was admitted to our emergency department due to a seizure. On physical examination, hypotonia, mild facial dysmorphism, brachydactyly of the 5th finger, prominent finger pads and pansystolic murmur were detected. A fasting glucose tolerance test was performed the next day due to her history of hypoglycemia, but she had convulsions at the fifth hour of the test. Her serum glucose was 24 mg/dL, insulin 1.94 mIU/L, C-peptide 0.94 ng/mL, growth hormone 11 ng/mL, anti-insulin antibody 4.2 IU/mL, cortisol 19.8 μg/dL, and adrenocorticotropic hormone 9.3 pg/mL. A diagnosis of hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia was considered. Given the abnormalities, genetic analysis for congenital hyperinsulinism, including the genes causing KS was performed. A heterozygous frameshift mutation (c.2579del, p.Leu860Argfs*70) was detected in the KMT2D gene. Epilepsy and other neurological symptoms may be seen in KS patients and in some of these the neurological symptoms are the result of hypoglycemia. In such cases, the detection and prevention of hypoglycemia can help prevent the progression of neurological symptoms. We suggest considering the diagnosis of KS for patients with hypoglycemia and dysmorphic features, even if the patient does not manifest all features of KS.
Keywords: Diazoxide; KDM6A; KMT2; Kabuki syndrome; hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia.
Figures
References
-
- Niikawa N, Matsuura N, Fukushima Y, Ohsawa T, Kajii T. Kabuki make-up syndrome: a syndrome of mental retardation, unusual facies, large and protruding ears, and postnatal growth deficiency. J Pediatr. 1981;99:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y, Suzuki Y, Chyo H, Hata A, Matsui I. A new malformation syndrome of long palpebral fissures, large ears, depressed nasal tip, and skeletal anomalies associated with postnatal dwarfism and mental retardation. J Pediatr. 1981;99:570–573. - PubMed
-
- Niikawa N, Kuroki Y, Kajii T, Matsuura N, Ishikiriyama S, Tonoki H, Ishikawa N, Yamada Y, Fujita M, Umemoto H, Iwama Y, Kondoh I, Fukushima Y, Nako Y, Matsui I, Urakami T, Aritaki S, Hara M, Suzuki Y, Chyo H, Sugio Y, Hasegawa T, Yamanaka T, Tsukino R, Yoshida A, Nomoto N, Kawahito S, Aihara R, Toyota S, Ieshima A, Funaki H, Ishitobi K, Ogura S, Furumae T, Yoshino M, Tsuji Y, Kondoh T, Matsumoto T, Abe K, Harada N, Miike T, Ohdo S, Naritomi K, Abushwereb AK, Braun OH, Schmid E, Opitz JM, Reynolds JF. Kabuki make-up (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome: a study of 62 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1988;31:565–589. - PubMed
-
- White SM, Thompson EM, Kidd A, Savarirayan R, Turner A, Amor D, Delatycki MB, Fahey M, Baxendale A, White S, Haan E, Gibson K, Halliday JL, Bankier A. Growth, behavior, and clinical findings in 27 patients with Kabuki (Niikawa-Kuroki) syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2004;127A:118–127. - PubMed
-
- Ng SB, Bigham AW, Buckingham KJ, Hannibal MC, McMillin MJ, Gildersleeve HI, Beck AE, Tabor HK, Cooper GM, Mefford HC, Lee C, Turner EH, Smith JD, Rieder MJ, Yoshiura K, Matsumoto N, Ohta T, Niikawa N, Nickerson DA, Bamshad MJ, Shendure J. Exome sequencing identifies MLL2 mutations as a cause of Kabuki syndrome. Nat Genet. 2010;42:790–793. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous