Delivering exceptionally safe transitions of care to older people: a qualitative study of multidisciplinary staff perspectives
- PMID: 32831038
- PMCID: PMC7444052
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-020-05641-4
Delivering exceptionally safe transitions of care to older people: a qualitative study of multidisciplinary staff perspectives
Abstract
Background: Transitions of care are often risky, particularly for older people, and shorter hospital stays mean that patients can go home with ongoing care needs. Most previous research has focused on fundamental system flaws, however, care generally goes right far more often than it goes wrong. We explored staff perceptions of how high performing general practice and hospital specialty teams deliver safe transitional care to older people as they transition from hospital to home.
Methods: We conducted a qualitative study in six general practices and four hospital specialties that demonstrated exceptionally low or reducing readmission rates over time. Data were also collected across four community teams that worked into or with these high-performing teams. In total, 157 multidisciplinary staff participated in semi-structured focus groups or interviews and 9 meetings relating to discharge were observed. A pen portrait approach was used to explore how teams across a variety of different contexts support successful transitions and overcome challenges faced in their daily roles.
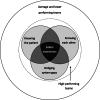
Results: Across healthcare contexts, staff perceived three key themes to facilitate safe transitions of care: knowing the patient, knowing each other, and bridging gaps in the system. Transitions appeared to be safest when all three themes were in place. However, staff faced various challenges in doing these three things particularly when crossing boundaries between settings. Due to pressures and constraints, staff generally felt they were only able to attempt to overcome these challenges when delivering care to patients with particularly complex transitional care needs.
Conclusions: It is hypothesised that exceptionally safe transitions of care may be delivered to patients who have particularly complex health and/or social care needs. In these situations, staff attempt to know the patient, they exploit existing relationships across care settings, and act to bridge gaps in the system. Systematically reinforcing such enablers may improve the delivery of safe transitional care to a wider range of patients.
Trial registration: The study was registered on the UK Clinical Research Network Study Portfolio (references 35272 and 36174 ).
Keywords: Elderly care; Focus groups; Health care professionals; Hospital discharge; Patient safety; Positive deviance; Qualitative; Transitions of care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Forster AJ, Murff HJ, Peterson JF, Gandhi TK, Bates DW. The incidence and severity of adverse events affecting patients after discharge from the hospital. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(3):161–167. - PubMed
-
- Healthwatch England . What do the numbers say about emergency readmissions to hospital? UK, Newcastle: Healthwatch England; 2017.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources